Understanding Thyroid Lump in Throat: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Introduction:
A thyroid lump in the throat can be a cause of concern for many individuals. While it is crucial to consult a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis, understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options can provide valuable insights. This article aims to shed light on thyroid lump symptoms, potential causes, and available treatment approaches in a simple and informative manner.
Thyroid Lump Symptoms:
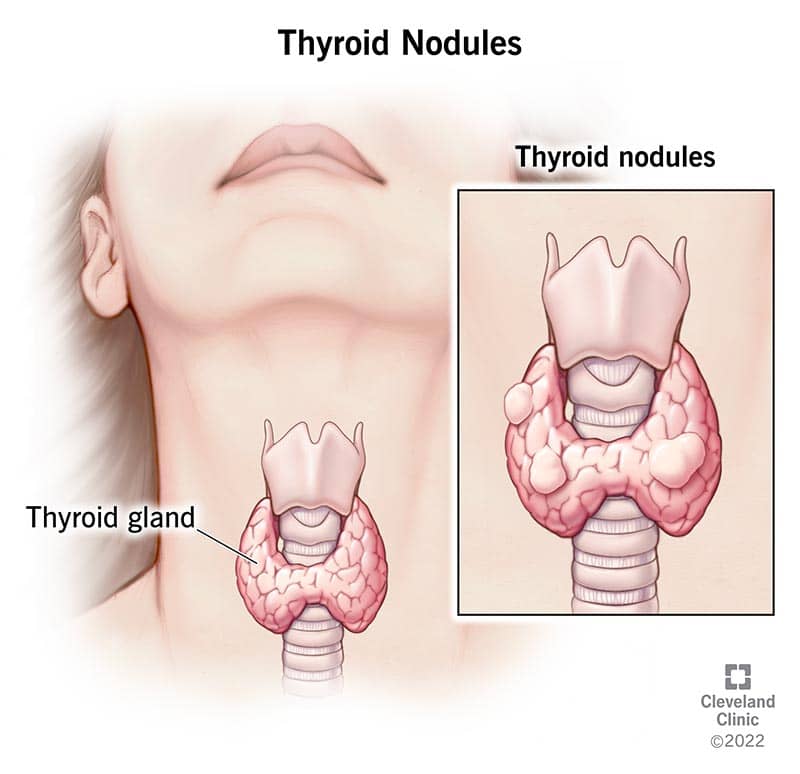
1. Swelling in the Neck: The most common sign of a thyroid lump is the presence of a visible or palpable swelling in the front of the neck.
2. Difficulty Swallowing: Some individuals may experience difficulty or discomfort while swallowing due to the enlarged thyroid gland.
3. Hoarseness or Voice Changes: The lump’s pressure on the vocal cords may lead to hoarseness or changes in the voice.
4. Breathing Difficulties: In some cases, a thyroid lump can cause breathing difficulties, especially when it grows larger and puts pressure on the windpipe.
5. Pain or Discomfort: The lump may cause pain or discomfort in the neck region, although this symptom is less common.
Causes of Thyroid Lumps:
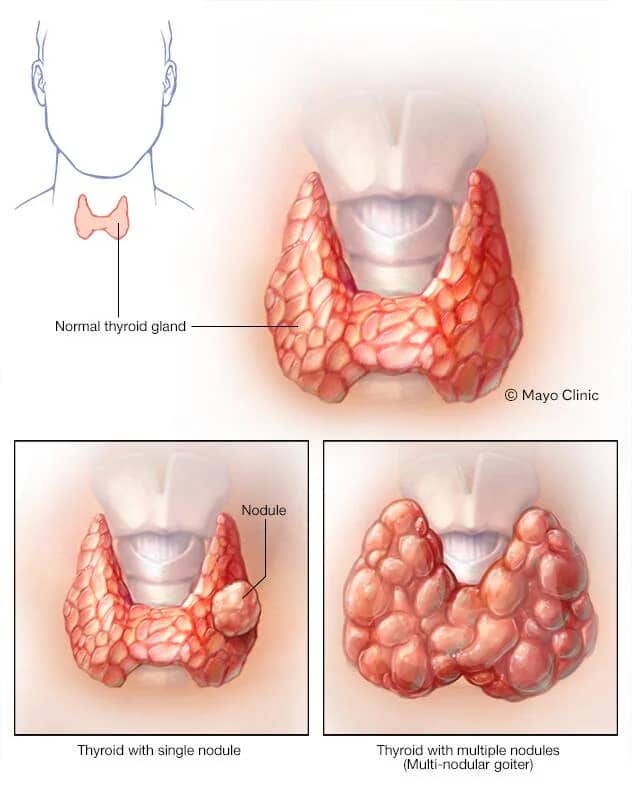
1. Thyroid Nodules: The most common cause of a thyroid lump is the presence of thyroid nodules, which are abnormal growths or lumps within the thyroid gland.
2. Goiter: Goiter refers to an enlarged thyroid gland, which can lead to the appearance of a lump in the throat.
3. Thyroid Cancer: While rare, a thyroid lump can be a sign of thyroid cancer. It is important to note that most thyroid nodules are benign and not cancerous.
Treatment Options:
1. Medical Evaluation: If you notice a lump in your throat, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough examination and accurate diagnosis.
2. Diagnostic Tests: Your doctor may recommend various tests, including ultrasound, blood tests, and fine-needle aspiration biopsy, to determine the nature of the lump.
3. Medication: In some cases, if the lump is noncancerous and not causing significant symptoms, your doctor may prescribe medication to manage the condition.
4. Surgery: If the thyroid lump is causing severe symptoms, growing rapidly, or is suspected to be cancerous, surgical removal of the lump or the entire thyroid gland may be necessary.
5. Radioactive Iodine Therapy: In cases where thyroid cancer is detected, radioactive iodine therapy may be recommended after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells.
What are the risk factors associated with thyroid nodules or thyroid lumps?
There are several risk factors associated with thyroid nodules or thyroid lumps, including:
1. Age: Thyroid nodules are more common in individuals over the age of 60.
2. Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop thyroid nodules.
3. Family History: There may be a genetic predisposition to developing thyroid nodules or thyroid cancer.
4. Radiation Exposure: Exposure to radiation, especially in childhood, can increase the risk of developing thyroid nodules or thyroid cancer.
5. Iodine Deficiency or Excess: Both iodine deficiency and excess can lead to the development of thyroid nodules.
6. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: An autoimmune disorder that can damage the thyroid gland, leading to the development of nodules.
7. Obesity: Obesity has been linked to an increased risk of developing thyroid nodules.
It is important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not necessarily mean that an individual will develop thyroid nodules or thyroid cancer. However, individuals with these risk factors should be vigilant in monitoring their thyroid health and consult a healthcare professional if they notice any concerning symptoms.
Symptoms of Thyroid Lump in Throat
A thyroid lump in the throat can manifest in various ways, and the symptoms may vary from person to person. Some common symptoms include:
- Visible lump or swelling: A noticeable lump or swelling in the neck, which may be tender to the touch.
- Neck pain or discomfort: Pain or discomfort in the neck, which can radiate to the jaw or ear.
- Difficulty swallowing: A feeling of tightness or constriction in the throat, making it hard to swallow food or liquids.
- Hoarseness or voice changes: Changes in the voice, such as hoarseness, raspy voice, or a strained voice.
- Coughing or choking: Coughing or choking sensations, especially when eating or drinking.
- Breathing difficulties: Shortness of breath or feeling of suffocation, especially when lying down or bending forward.
- Fatigue or weakness: Unexplained fatigue, weakness, or lethargy.
- Weight changes: Unintended weight loss or gain, despite no changes in diet or exercise.
- Heat or cold intolerance: Increased sensitivity to heat or cold, leading to sweating, flushing, or chills.
- Nervousness or anxiety: Feeling anxious, nervous, or irritable, which can be a result of hormonal imbalances.
Diagnosis of Thyroid Lump in Throat
To diagnose a thyroid lump in the throat, a doctor may perform the following tests:
- Physical examination: A thorough examination of the neck and thyroid gland to feel for any lumps or swelling.
- Imaging tests: Ultrasound, CT, or MRI scans to visualize the thyroid gland and detect any abnormalities.
- Thyroid function tests: Blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels and detect any hormonal imbalances.
- Biopsy: A sample of tissue from the thyroid gland to examine for cancer cells or other abnormalities.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Lump in Throat
The treatment of a thyroid lump in the throat depends on the underlying cause and the size of the lump. Some common treatment options include:
- Watchful waiting: Monitoring the lump with regular check-ups and imaging tests to ensure it does not grow or change.
- Surgery: Removing the thyroid gland or the affected portion of the gland to treat cancer or nodules.
- Radioactive iodine therapy: Using radioactive iodine to shrink the thyroid gland or destroy cancer cells.
- Medications: Prescribing medications to treat hormonal imbalances, such as thyroid hormone replacement therapy.
- Thyroid hormone suppression therapy: Using medications to reduce the production of thyroid hormone and shrink the thyroid gland.
Conclusion
A lump in the thyroid is a symptom often associated with concern in the throat, although most thyroid nodules are benign. It is, therefore, very important to remind oneself that consulting a health professional is important if there is to be an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment. Early detection and management can alleviate symptoms and make sure people with thyroid lumps have the best prognosis.