Table of Contents
ToggleMy Thyroid Gland Goiter Treatment: A Comprehensive Overview
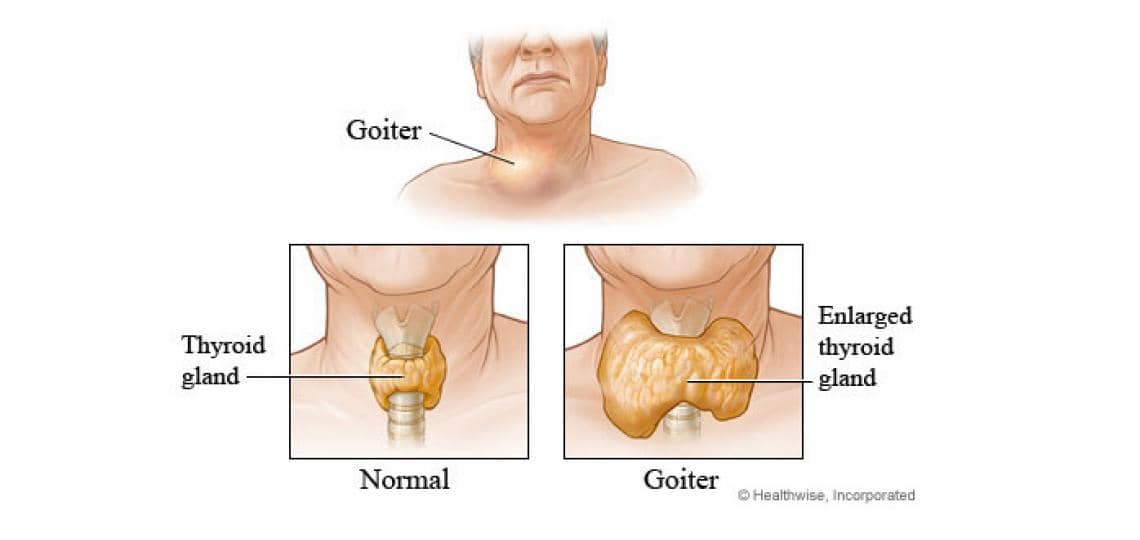
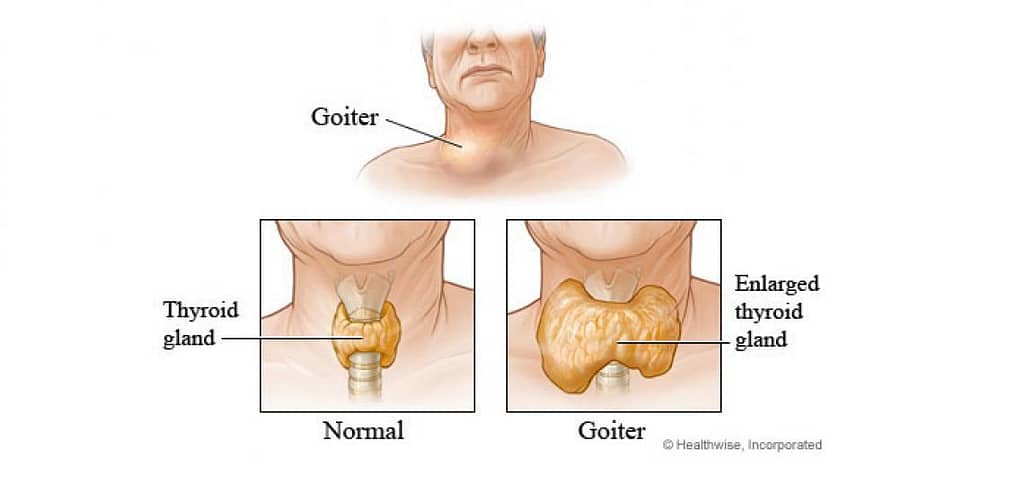
Generally, the butterfly-shaped organ is found in the neck and is very small, but the thyroid gland is responsible for regulating many bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and development. On the other hand, this gland sometimes becomes swollen and is termed a goiter. In this article, we are going to explore the causes, symptoms, and management strategies of goiter of the thyroid gland.
What is Thyroid Gland Goiter?
A goiter is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland, which can occur for various reasons. The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, and an enlarged gland can lead to overproduction or underproduction of these hormones. Goiter can be classified into two types:
- Diffuse goiter: The entire thyroid gland is enlarged, leading to a uniform swelling in the neck.
- Nodular goiter: The thyroid gland contains one or more nodules, which are abnormal growths that can be benign or cancerous.
Causes of Thyroid Gland Goiter
Several factors can contribute to the development of thyroid gland goiter, including:
- Iodine deficiency: Iodine is essential for the production of thyroid hormones. A lack of iodine in the diet can lead to an enlarged thyroid gland.
- Thyroid hormone imbalance: An imbalance of thyroid hormones, such as hyperthyroidism (too much thyroid hormone) or hypothyroidism (too little thyroid hormone), can cause the thyroid gland to enlarge.
- Autoimmune disorders: Conditions such as Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis cause the immune system to become activated against the thyroid gland, resulting in inflammation and enlargement.
- Thyroid nodules: Benign or cancerous growths on the thyroid gland can cause it to enlarge.
- Radiation exposure: Exposure to radiation, particularly in the neck area, can increase the risk of developing thyroid gland goiter.
- Genetics: A family history of thyroid disorders can increase the risk of developing goiter.
Symptoms of Thyroid Gland Goiter
Goiter of the thyroid gland Symptoms of goiter of the thyroid gland The symptoms associated with goiter of the thyroid gland depend upon the underlying causes and size of the goiter.
The common symptoms include:
- Neck swelling: a visible swelling in the neck that can be painless or tender to the touch.
- Difficulty swallowing: Compression of the esophagus by the enlarged thyroid gland can lead to difficulty swallowing.
- Breathing difficulties: Compression of the trachea by the enlarged thyroid gland can lead to breathing difficulties.
- Thyroid hormone imbalance symptoms: Symptoms of hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism, such as weight changes, fatigue, hair loss, or mood changes.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Gland Goiter
The treatment of thyroid gland goiter depends on the underlying cause, size of the goiter, and symptoms. Treatment options include:
- Thyroid hormone replacement therapy: Hypothyroidism may be managed by administering thyroid hormone replacement medication to correct the level of thyroid hormones in the body.
- Antithyroid medications: These drugs are used to treat hyperthyroidism, whereby they can reduce the overall production of hormones.
- Radioactive iodine therapy: The attempt to shrink the thyroid gland by swallowing a radioactive iodine pill through a therapy called radioactive iodine therapy.
- Surgery: These may be performed for large goiters or for those that prove to be cancerous.
- Thyroid nodule removal: This is performed when the nodules are cancerous or symptomatic.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Thyroid Gland Goiter
Other than medical treatment, lifestyle changes help manage the goiter of the thyroid gland.
- Iodine-rich diet: Seafood, dairy, and even iodized salt are all excellent sources of food to keep the thyroid healthy
- Healthy weight management: Healthy weight management can reduce the risk of developing thyroid gland goiter.
- Stress management: Yogic or meditation techniques may aid in managing the symptoms of a hormonal imbalance.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity is likely to help keep general health improved and give less opportunity for a thyroid gland goiter to develop.
how to shrink a goiter naturally
Naturally, there are some home remedies and lifestyle changes that can help combat underlying thyroid problems, provided the goiter has developed a benign condition. However, one must always consult first with a healthcare professional before attempting to treat a goiter naturally.
Here are some natural approaches that may be helpful:
- Iodine-rich foods: Swallowing iodine-rich foods such as seaweed, kelp, seafood, dairy products, and iodized salt can help support the thyroid and potentially reduce the size of goiters.
- Selenium-rich foods: Elenium is a very important mineral that helps protect the thyroid gland from damage. Sources that are rich in selenium include Brazil nuts, fish, turkey, and beef.
- Ashwagandha: This herb may be adaptogenic and hence reduce stress and anxiety, contributing to some imbalance in thyroid functioning. Ashwagandha may also regulate the production of thyroid hormones.
- Bladderwrack: This seaweed is iodine-rich and might support thyroid function. Consult a healthcare professional before using bladderwrack because it interacts with some medications.
- Turmeric: The natural anti-inflammatory properties of turmeric reduce the inflammation of the thyroid gland due to its curcumin compound.
- Guggul: This herb has been used in Ayurvedic medicine to support thyroid function and may help reduce goiter size.
- Castor oil: Applying castor oil topically to the thyroid area could provide relief by reducing inflammation and discomfort.
- Thyroid-supporting supplements: Some supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and probiotics, have been observed to enhance thyroid function along with regular nutritional needs. Of course, always consult a doctor before starting any new supplements.
- Dietary changes: Healthy foods that reduce inflammation and contain antioxidants, fiber, and omega-3 fatty acids can promote health.
- Stress management: Stress may aggravate extremely high levels of the problem. Practice stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing to help you cope with stress.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate thyroid hormone production and overall health.
- Avoid soy and cruciferous vegetables: Soy products and cruciferous vegetables—broccoli, cauliflower, and kale—should be taken in moderation or avoided since they affect thyroid function. Goiters will be avoided by avoiding them.
- Avoid fluoride: High excess fluoride consumption can cause problems in the thyroid. Use fluoride-free toothpaste and avoid water that is fluoridated.
- Get enough vitamin B12: A deficiency of vitamin B12 has been associated with problems in the thyroid gland. Take note that you get enough in your diet or supplements.
- Consider thyroid massage: gentle massaging techniques may increase blood flow and decrease inflammation in the area of the thyroid. Consult a health care professional before trying to massage the thyroid.
Conclusion
Treatment for goiters depends on its cause and severity. Small, non-problemsome goiters are often left untouched. Treatment for a condition of iodine deficiency goiters usually includes dietary changes or supplementation with iodine. Medications can control hormonal imbalances caused by goiters. In some cases, the goiter may be reduced in size through radioactive iodine ablation or surgery to rectify the problems in the functioning of the thyroid. A doctor should be consulted to determine the appropriate treatment.