The Cure for Autoimmune Disease: A Step-by-Step Guide

Introduction
Autoimmune diseases are illnesses where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues and organs. These illnesses cause a lot of discomfort, damage to organs, and fatigue. Since there is no definite cure for autoimmune diseases, recent discoveries in science have offered hope for managing these conditions more effectively.
The Breakthrough Therapy
In a breakthrough that has probably been waiting for, researchers have developed a therapy using genetically modified cells to send severe autoimmune diseases into remission.
Let’s delve into the details:
- The patients: five young adults between the ages of 18-24 years, all suffering from a severe form of lupus-an autoimmune disease that can affect the heart, lungs, brain, and kidneys.
- Treatment: These patients were recipients of genetically modified immune cells. These were genetically engineered to hunt and kill the patient’s own B cells. In lupus, B cells produce autoantibodies that attack healthy tissues instead of defending against pathogens.
- Results: All five patients experienced remission after the therapy. They have been off lupus medication for three to 17 months. Symptoms like arthritis, fatigue, and heart valve fibrosis significantly improved.
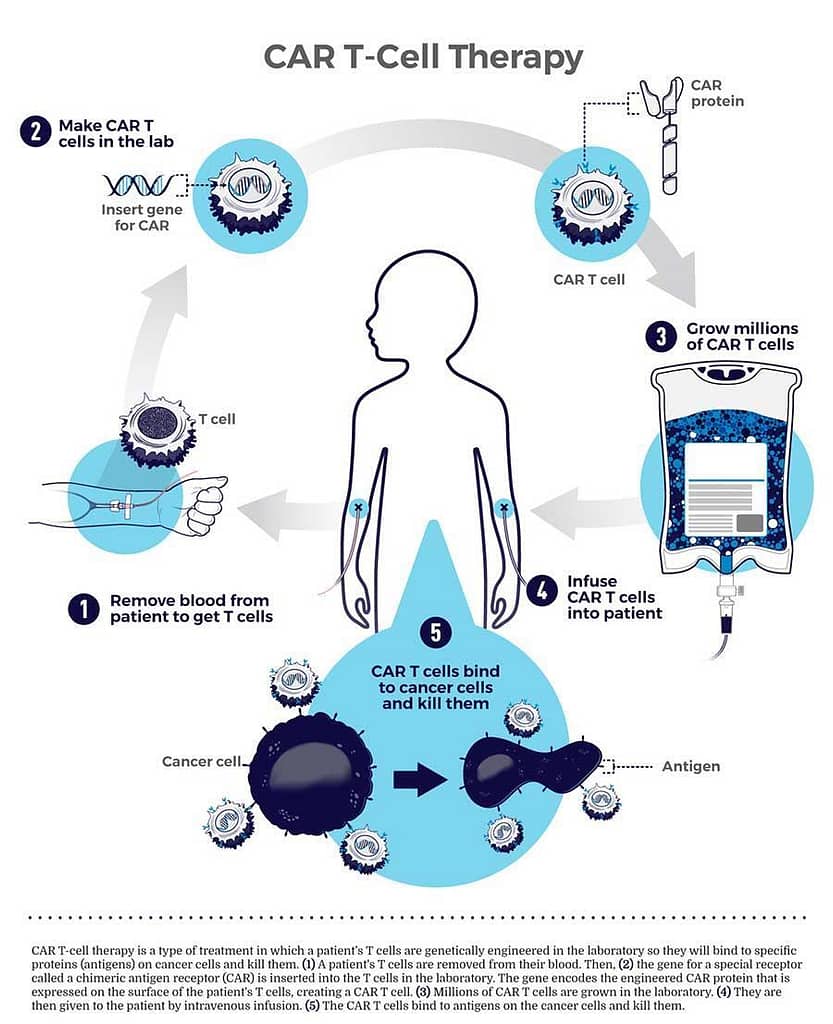
What Is CAR T-Cell Therapy?
- CAR T-cell therapy has been successful in treating certain cancers since 2015. Here’s how it works:
- Collect the patient’s T-cells (essential components of the immune system).
- Genetically modify these T-cells to target specific cells (in this case, the aberrant B cells in lupus).
- Infuse the modified T-cells back into the patient’s body.
Hope for Other Autoimmune Conditions
- The success with lupus patients raises optimism for treating other autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
- While more research is needed, this breakthrough offers a glimmer of hope for those battling autoimmune conditions.
What are some natural ways to manage autoimmune diseases?
These are some effective home remedies and lifestyle adjustments to reduce the symptoms and improve your overall well-being:
- Fish Oil: Fish oil is rich in omega-3 fats and is anti-inflammatory. A spoonful of fish oil a day or 500 mg of fish oil capsules a day can help reduce inflammation from immune responses.
- Vitamin D: Adequate levels of vitamin D are important in maintaining immunity. A deficiency increases the risk of autoimmune disorders. Consult with your physician as to whether vitamin D supplements should be considered.
- Coconut Oil: Apply coconut oil to your skin to make use of its anti-inflammatory and anesthetic properties. The lauric acid of coconut oil is the reason behind such therapeutic properties.
- Green Tea: Epigallocatechin gallate, an active compound in green tea, helps reduce inflammation. Drinking a cup of green tea every morning on an empty stomach can be beneficial.
- Turmeric: Curcumin in turmeric is a potent anti-inflammatory agent. Incorporate turmeric into your diet by adding it to smoothies or dishes.
- Yoga and Meditation: Yoga and meditation have shown positive effects in managing autoimmune conditions. They help reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
- Supplements: Consider supplements like glutathione, curcumin, N-acetyl cysteine, probiotics, and omega-3 to reduce the inflammation resulting from autoimmunity.
- Anti-Inflammatory Foods: Add turmeric, ginger, and omega-3 sources such as walnuts or chia seeds to your diet. These changes can significantly make a difference over time.
- Comprehensive Approach: Address the five key levers for managing autoimmune diseases:
- Nutrition: Choose anti-inflammatory foods.
- Gut Health: Support a healthy gut microbiome.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques.
- Sleep: Prioritize quality sleep.
- Detoxification: Support your body’s natural detox processes.
- Herbal Remedies: Find out about immune-modulating herbs. Herbal remedies can help with autoimmune disorders.
Remember, individual responses may vary, and always seek the advice of a healthcare professional if serious changes in a lifestyle are going to be undertaken or any new supplementation is begun. Above all, always remember to consider your general health and well-being.
Tell me more about gut health and autoimmune diseases.
Autoimmune diseases have raised the importance of gut health. It is of paramount importance to the processes of the gut microbiome. These are the trillions of bacteria that live within the intestinal tract and play an important role in regulating the immune system. This is due to disruption of the balance of gut bacteria, a well-known result of autoimmune diseases.
Here are some of the ways gut health can influence autoimmune diseases:
- Gut Basics:
- The gut microbiome, often referred to as our “second brain,” plays a pivotal role in overall health and immunology.
- It consists of trillions of microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, and fungi) residing primarily in the human gut.
- These microorganisms influence digestion, vitamin synthesis, and immune system training.
- Key players include probiotics (like lactobacillus) and beneficial bacteria.
- Microbial Diversity:
- A healthy gut boasts diverse microbial species.
- Notable probiotics, like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, contribute to gut health.
- These bacteria break down food, produce essential nutrients, and protect against harmful pathogens.
- Maintaining microbial diversity helps reduce intestinal permeability and colitis.
- Dysbiosis and Autoimmune Diseases:
- Dysbiosis refers to an imbalance in the gut microbiota.
- It has been associated with many health problems, such as obesity, diabetes, rheumatism, and autoimmune diseases.
- Autoimmune conditions occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s cells.
- Studies show that dysbiosis is associated with autoimmune diseases like lupus and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- The Immune System and Gut Lining:
- About 80% of our immune system resides within the gut lining.
- Imbalances in the gut microbiome can contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases.
- When dysbiosis occurs, the immune system may misidentify self-cells as harmful invaders, leading to autoimmune responses.
- Strategies for Gut Health:
- Probiotics: Consuming probiotic-rich foods (like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut) supports gut health.
- Fermented Foods: Incorporate kimchi, kombucha, and other fermented foods for beneficial gut bacteria.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated aids digestion and maintains gut function.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress negatively impacts gut health, so practice relaxation techniques.
- Balanced Diet: Prioritize whole foods, fiber, and prebiotics (which feed beneficial gut bacteria).
- Holistic Approach:
- Addressing gut health involves a comprehensive approach.
- Optimize your gut microbiome to support overall well-being and reduce the risk of autoimmune diseases.
Conclusion
There is no cure for autoimmune diseases, but recent research in gut health holds promising possibilities for treatment in the future. Individuals with autoimmune diseases can retain a healthy gut microbiome through diet and future probiotic treatment, which can lead to reduced symptoms and improved general health.