Diabetes in Women Over 40: A Comprehensive Guide
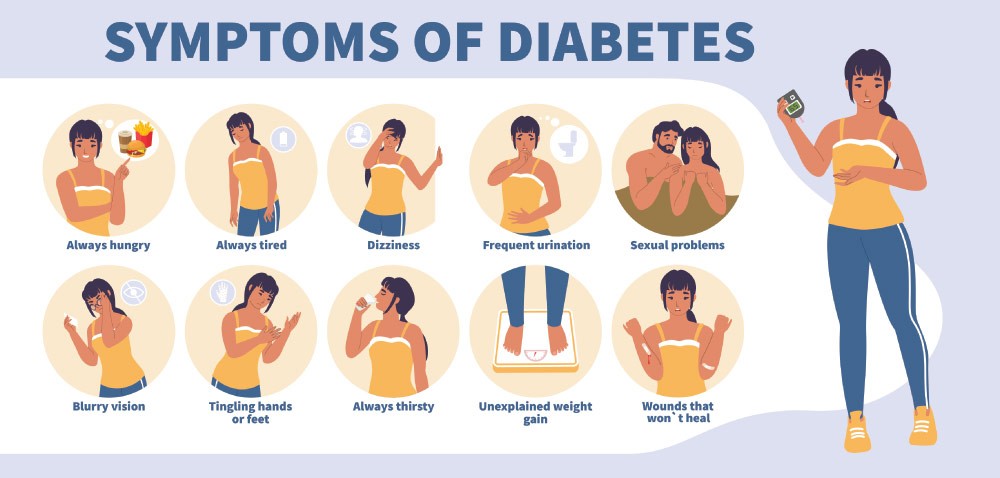
One in ten women over the age of 40 is at risk of developing diabetes, a statistic that might surprise even seasoned healthcare professionals. The subtle but pervasive symptoms often begin with increased thirst or a slightly blurry vision, easily dismissed as signs of aging. Yet, these could be the first indicators of a much larger issue.
Historically, symptoms in women such as fatigue, weight fluctuations, and frequent infections have been overlooked or misattributed. Recent studies indicate that these signs are critical alarms in diagnosing diabetes early. Lifestyle modifications and proactive monitoring can make significant differences in managing this condition.

Source: wp.com
Recognizing the Common Symptoms of Diabetes in Women Over 40
Frequent Urination and Increased Thirst
One of the most noticeable signs is frequent urination. Women might find themselves needing to go to the bathroom more often, especially at night. This is usually paired with an increased thirst.
The body tries to get rid of the extra sugar by making more urine, leading to dehydration. This can make you feel thirsty all the time. Pay attention if you feel unusually thirsty or find yourself drinking water more frequently.
Unexplained Weight Loss and Fatigue
Women over 40 might experience unexpected weight loss even without trying. This happens because the body cannot properly use glucose for energy.
As a result, it starts breaking down muscle and fat for fuel. Fatigue is another common symptom, as the cells are not getting the energy they need. Feeling tired after doing simple tasks could be an indication of diabetes.
Blurred Vision
High blood sugar levels can cause the lens of the eye to swell. This can lead to blurred vision.
Some women ignore this symptom, thinking it’s just due to aging. If you notice changes in your vision, it’s worth discussing with a healthcare provider.
Frequent Infections and Slow-Healing Wounds
Women with diabetes are more prone to infections. High blood sugar levels make it harder for the body to fight off germs.
Common infections include urinary tract infections and yeast infections. Slow-healing wounds, especially on the feet, are also a red flag.
Hi9 | How does Diabetes after women age of 40? | Dr. Lakshmi Lavanya Alapati | Endocrinologist
Understanding the Role of Age and Hormonal Changes in Diabetes
The risk of diabetes significantly increases as women age, due to changes in hormones and metabolism. These changes can affect insulin sensitivity, making the body less effective at regulating blood sugar. Hormonal changes during menopause further complicate this process.
The Impact of Menopause
During menopause, women experience a decrease in estrogen levels. This hormone plays a vital role in maintaining insulin sensitivity. As estrogen drops, blood sugar levels can become harder to control.
Hot flashes and night sweats are common symptoms that also cause stress. Stress hormones like cortisol can increase blood sugar levels, making diabetes management more challenging.
Changes in Body Composition
Aging and hormonal changes also lead to shifts in body composition. Women tend to lose muscle mass and gain more abdominal fat as they age. Both of these changes affect how the body handles glucose.
Muscle cells are more effective at using glucose for energy compared to fat cells. Less muscle and more fat can lead to higher blood sugar levels and increased diabetes risk.
Genetic Factors
Genetics also play a key role in diabetes risk as women age. If there is a family history of diabetes, the likelihood of developing the disease increases. This genetic predisposition can interact with hormonal and metabolic changes.
Although genetics can’t be changed, understanding these risks can help women take proactive steps. Regular screenings and lifestyle adjustments can make a significant difference.
Navigating the Misconceptions and Myths about Diabetes in Women
Many people think that only those who are overweight can get diabetes, but that’s a myth. Women of all body types can develop diabetes. It’s not just about weight; genetics and lifestyle also play crucial roles.
Another common misconception is that diabetes is not a serious disease. This is far from true, as unmanaged diabetes can lead to severe complications. These complications include heart disease, kidney damage, and vision problems.
Many believe that eating too much sugar directly causes diabetes. While diet is important, it’s more about overall lifestyle and genetics. A balanced diet and regular exercise are key to managing and preventing diabetes.
Some think that insulin treatment means a woman has failed to manage her diabetes. In reality, insulin can be a necessary and effective part of treatment. Timely use of insulin helps manage blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
Interpreting Diabetes Risk Factors in Women Over 40
Genetic factors play a significant role in increasing the risk of diabetes in women over 40. If a woman has a family history of diabetes, her chances of developing the disease are higher. This is why understanding your family medical history is crucial.
Lifestyle choices also significantly impact diabetes risk. Poor diet, high in sugary and fatty foods, can lead to obesity, which is a major risk factor. Regular physical activity helps lower this risk by maintaining a healthy weight.
Hormonal disorders like PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) increase the risk of diabetes. Women with PCOS often experience insulin resistance, leading to higher blood sugar levels. Monitoring and managing PCOS can help reduce the risk.
Certain ethnic backgrounds have a higher predisposition to diabetes. For example, African American, Hispanic, Native American, and Asian women are more prone to the disease. Acknowledging these inherent risks helps in taking preventive measures early on.
Women who had gestational diabetes during pregnancy are at higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. It’s essential for these women to maintain a healthy lifestyle post-pregnancy. Regular glucose monitoring can help in early detection.
Age itself is a significant risk factor. As women get older, their bodies become less efficient at using insulin. Being aware of all these risk factors can encourage proactive health care and prevention strategies.
Proactive Steps Towards Early Detection and Management of Diabetes
Regular check-ups are essential for early detection of diabetes. Blood tests such as the A1C can reveal your average blood sugar levels over the past three months. Early detection allows for timely intervention and better management.
Maintaining a healthy diet is crucial. Focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Avoid processed foods and high-sugar snacks to keep your blood sugar levels stable.
Regular physical activity can help manage diabetes effectively. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can make a big difference in blood sugar control.
Monitoring your blood sugar levels at home can help you keep track of your condition. Use a blood glucose meter to check your levels at different times of the day.
- Fasting blood sugar test
- Post-meal testing
- Bedtime blood sugar test
Consulting healthcare professionals regularly is important for managing diabetes. They can provide guidance on medication, lifestyle changes, and any necessary adjustments. Regular visits can help prevent complications and ensure that your treatment plan is effective.
Stay educated about diabetes. Understanding the condition helps you make informed choices about your health. Read reliable sources and ask your doctor questions to stay up-to-date.
Key Takeaways
- Increased thirst is a common sign of diabetes in women over 40.
- Frequent urination can indicate high blood sugar levels.
- Unexplained weight loss may be an early warning sign of diabetes.
- Blurry vision and frequent infections are also symptoms to watch for.
- If wounds heal slowly, it might be time for a medical check-up.
Source: alldaychemist.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding diabetes is crucial as it affects many people, especially women over 40. Below are some common questions and answers on this topic.
1. What are the initial symptoms of diabetes in women?
Initial symptoms of diabetes in women can be subtle. Many experience increased thirst and frequent urination at first. These symptoms occur because high blood sugar levels cause the body to lose more fluid.
Other early signs include unexplained weight loss and fatigue. If you notice these changes, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
2. How does age affect the risk of developing diabetes?
The risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases as you get older. This happens because aging can lead to decreased insulin sensitivity and more metabolic issues. Women over 40 should be more vigilant about their diet and exercise.
Hormonal changes during menopause also play a role in higher diabetes risks. Being aware of these factors can help with early detection and effective management.
3. Can lifestyle changes prevent diabetes in women over 40?
Yes, lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetes. Eating a balanced diet low in sugary foods is crucial for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
Regular physical activity also helps keep your weight in check and improves insulin sensitivity. Simple habits like daily walks or gardening can make a big impact on your health.
4. Are there specific risk factors for diabetes that women over 40 should be aware of?
Certain factors raise the risk of developing diabetes, such as family history and obesity. Women who had gestational diabetes during pregnancy are also at a higher risk later in life.
A sedentary lifestyle contributes significantly to this condition too. Being proactive by knowing these risk factors helps in taking preventative measures early on.
5. What medical tests diagnose diabetes effectively?
The most common test is the A1C test, which shows average blood sugar levels over three months. Another effective test is the fasting plasma glucose test (FPG), which measures blood sugar after an overnight fast.
Your doctor might also recommend an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). This involves drinking a sugary liquid followed by several blood tests to track how your body handles glucose over time.
7 Early Signs Of Diabetes In Women Over 40
Conclusion
Understanding the signs of diabetes in women over 40 is essential for early detection and effective management. By recognizing symptoms like increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss, women can seek timely medical advice. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the risk of complications.
Age and hormonal changes play a critical role in diabetes risk, making it vital to stay informed and vigilant. Regular check-ups, a balanced diet, and consistent exercise are key steps toward maintaining good health. Remember, early detection and lifestyle adjustments can make all the difference.