How to Recognize Chlamydia Symptoms in Women
One startling fact about chlamydia is that it remains one of the most common sexually transmitted infections globally, yet many women remain unaware of its symptoms. One of the primary indicators for women is unusual discharge, which can often be mistaken for other less severe conditions. Immediate attention to these signs can provide better outcomes in managing the infection.
Historically, cervical infections like chlamydia have been underreported due to the stigma and lack of education surrounding sexual health. Studies indicate that 70-90% of women with chlamydia experience abnormal discharge, an alarming statistic that underscores the need for awareness and timely medical intervention. Regular screenings and early detection remain crucial in mitigating long-term health repercussions.
Source: clevelandclinic.org
Defining Chlamydia: An Overview
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by bacteria. It affects both men and women but often occurs without noticeable symptoms. Left untreated, it can lead to serious health problems.
The bacteria responsible for chlamydia is called *Chlamydia trachomatis*. It primarily spreads through vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who is infected. Using protection during sex can greatly reduce the risk of transmission.
Many people with chlamydia do not realize they are infected because the symptoms can be mild or not present at all. This lack of obvious symptoms makes regular testing especially important.
If symptoms do occur, they usually appear within weeks of exposure. Chlamydia can cause pain and discomfort, especially during urination. Both local health departments and private clinics offer testing services.
Transmission Methods of Chlamydia
Chlamydia spreads through sexual contact with an infected person. Engaging in unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex increases the risk. Using condoms and dental dams can provide protection.
In rare cases, a mother with chlamydia can pass the infection to her baby during childbirth. This can lead to complications such as eye infections or pneumonia in the newborn. Pregnant women are advised to undergo screening and treatment.
It’s important to note that chlamydia can still spread even if an infected person doesn’t have symptoms. Regular testing and safe sex practices are crucial in preventing the spread of this infection.
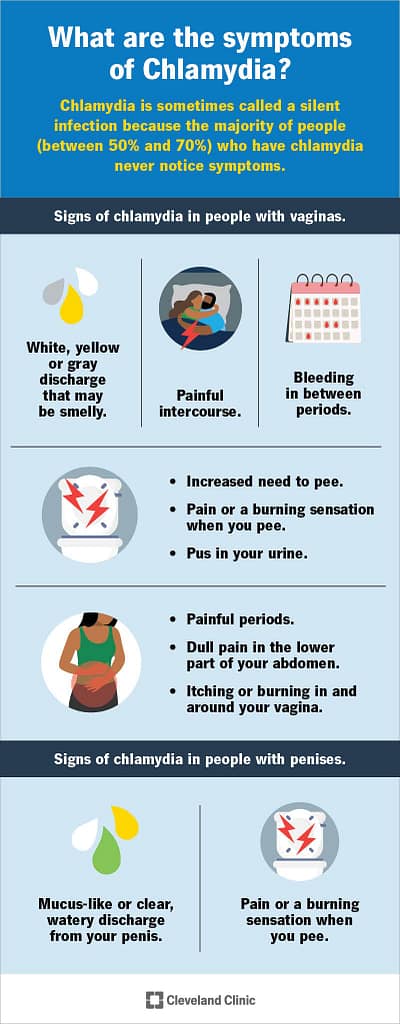
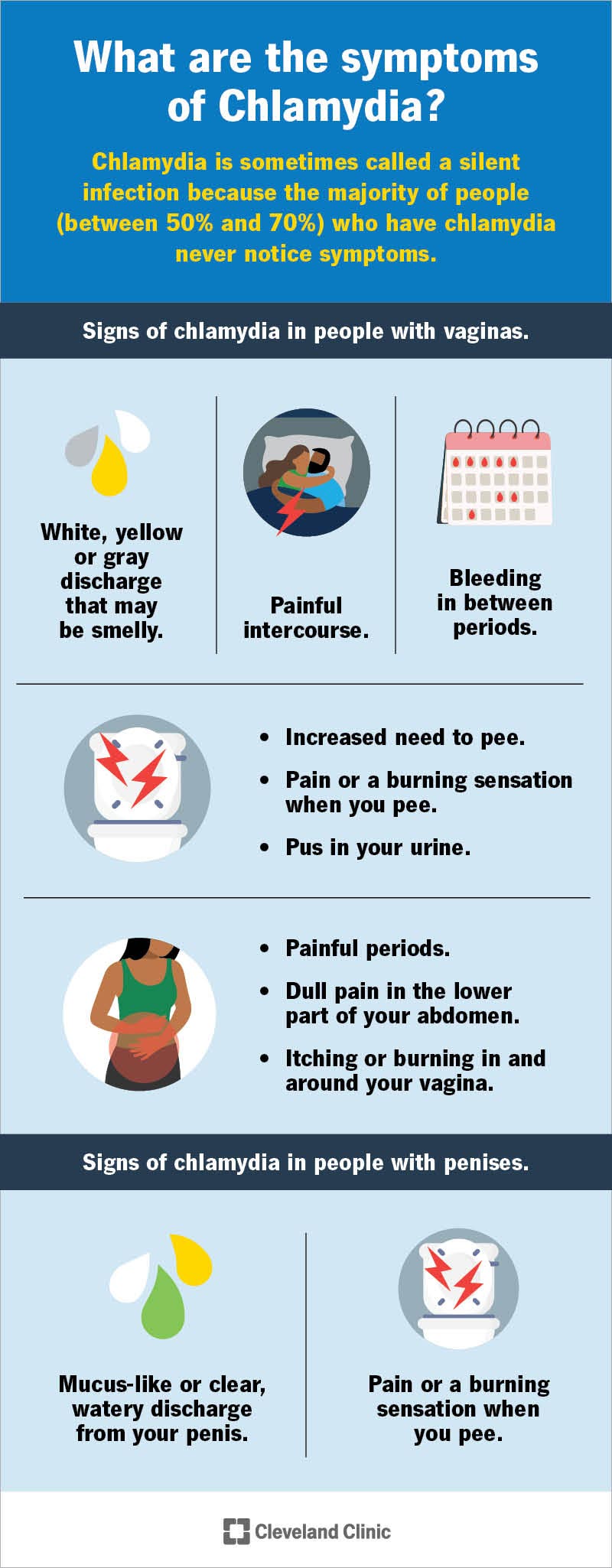
Symptoms of Chlamydia in Women
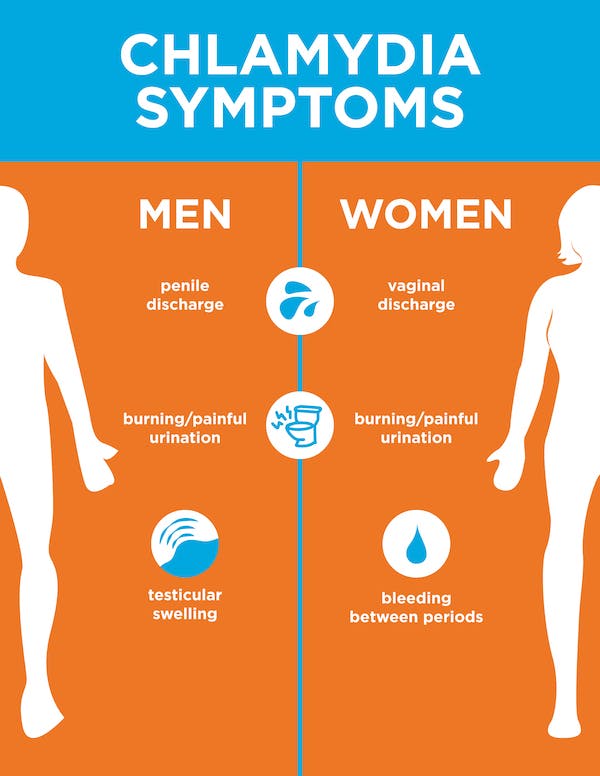
Women with chlamydia often experience unusual vaginal discharge. The discharge may be yellowish or have a strong smell. Other symptoms include pain during sex or urination.
Pelvic pain and bleeding between periods can also be signs of chlamydia. If left untreated, the infection can cause severe reproductive problems. This includes pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can lead to infertility.
Regular check-ups and early diagnosis can prevent these complications. Women should seek medical attention if they experience any unusual symptoms.
Importance of Regular Screenings
Regular screenings are essential for the early detection of chlamydia. Since many people do not show symptoms, relying on symptoms alone is not enough. Regular testing helps ensure timely treatment.
Healthcare providers recommend annual screenings for sexually active individuals, especially those under 25. Screening is also advised for pregnant women and people with multiple sexual partners.
Early detection through regular screenings can help prevent long-term health issues. Timely treatment ensures effective management of the infection and reduces the risk of transmission.
Chlamydia | Top 5 Symptoms Experienced by Men and Women
Understanding Symptoms of Chlamydia in Women
Chlamydia is often called a “silent” infection because its symptoms can be mild or absent. This makes it tricky to diagnose without testing. However, several symptoms can help identify the infection.
Unusual Vaginal Discharge
One of the most common signs of chlamydia in women is unusual vaginal discharge. This discharge may be yellowish and have a strong odor. Women should note any changes in their discharge and seek medical advice.
Vaginal discharge due to chlamydia may also be more abundant than usual. Good awareness of one’s body can help in recognizing these changes early. Early detection can lead to more effective treatment.
Pain and Discomfort
Women with chlamydia often experience pain during urination. This pain can range from mild to severe. Sometimes, there is also discomfort during sexual intercourse.
Pelvic pain can be another symptom of chlamydia. This pain might be mistaken for menstrual cramps but should not be ignored if persistent. Regular check-ups are vital for early diagnosis.
Bleeding and Other Symptoms
Chlamydia can cause bleeding between menstrual periods. This unusual bleeding is a warning sign that should prompt medical attention. Ignoring it can lead to complications.
Other symptoms may include fever and lower abdominal pain. These symptoms are less common but are still significant. Seeking medical advice promptly ensures timely treatment and prevents further issues.
Knowing and understanding these symptoms is crucial. Regular screenings and being aware of any changes in your body can help in early detection. Visit trusted sources like the CDC for more information on chlamydia symptoms and prevention.
The Significant Role of Discharge in Identifying Chlamydia
Detecting chlamydia often hinges on noticing unusual vaginal discharge. This discharge may appear yellowish or cloudy. The change in color and consistency is a key indicator.
Understanding what is normal for your body is crucial. Regularly checking for unusual discharge can help catch chlamydia early. This early detection can prevent severe complications.
Vaginal discharge linked to chlamydia may also be accompanied by a strong odor. This odor can sometimes be unpleasant or fishy. Any sudden change in your discharge’s smell warrants a medical consultation.
A comprehensive approach to monitoring discharge involves paying attention to its volume. Increased discharge can be a clear sign of infection. Keeping track can aid in timely medical intervention and treatment.
The Importance of Early Detection and Regular Screenings
Chlamydia often lacks noticeable symptoms, making early detection crucial. Regular screenings can identify the infection before serious health problems arise. This is especially vital for sexually active individuals.
Women under 25 and those with multiple partners should get annual screenings. Early detection through regular testing can prevent complications such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID can cause chronic pain and infertility.
Healthcare providers recommend more frequent screenings for people with higher risk factors. These include having a new partner or not using protection consistently. Knowing your status helps keep you and your partners healthy.
Screenings are simple and involve a swab or urine test. The process is quick, and results can help guide effective treatment. Treatment usually involves antibiotics, making early detection straightforward and manageable.
Consistent screenings can also reduce the spread of chlamydia. When detected early, infected individuals can take steps to avoid transmitting the disease. This benefits both personal and public health.
Most importantly, regular check-ups foster a proactive approach to sexual health. Staying informed and vigilant can lead to better health outcomes and peace of mind. Planned Parenthood provides valuable resources for screening and prevention.
Treatment and Prevention of Chlamydia
Treating chlamydia is straightforward with the right antibiotics. The infection typically clears up within a week or two. Following your doctor’s prescription is essential for effective treatment.
Commonly prescribed antibiotics include azithromycin and doxycycline. Both are highly effective in eliminating the bacteria. Avoiding sexual activity during treatment is crucial to prevent spreading the infection.
- Azithromycin: Usually given as a single dose
- Doxycycline: Taken as a longer course, typically 7 days
Preventing chlamydia largely relies on practicing safe sex. Using condoms can significantly reduce the risk of transmission. Regular screenings also play a vital role in prevention.
Educating yourself and your partner about sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can help maintain sexual health. Open communication is key to ensuring mutual understanding and preventive measures. Knowledge is a powerful tool in preventing STIs.
Getting regular check-ups and encouraging partners to do the same is beneficial. This promotes a proactive approach to health. It ensures that any potential infections are caught and treated early.
Key Takeaways
- Chlamydia often shows mild or no symptoms in women.
- Vaginal discharge can be yellowish with a strong odor.
- Pain during urination or sex is common in chlamydia cases.
- Pelvic pain and unusual bleeding are other key symptoms.
- Regular screenings are crucial for early detection and treatment.
Source:
Frequently Asked Questions
Get answers to some of the most common questions about chlamydia in women. Learn about symptoms, treatment, and prevention.
1. How is chlamydia detected?
Chlamydia is detected through a simple test, usually a swab from the cervix or urethra, or a urine sample. The collected sample is then analyzed in a lab to check for the presence of Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria.
It’s recommended to get screened regularly if you’re sexually active. Regular testing helps catch the infection early, providing timely treatment and preventing complications like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
2. Can chlamydia be cured?
Yes, chlamydia can be cured with antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare provider. Common antibiotics used include azithromycin taken as a single large dose or doxycycline taken over seven days.
However, it’s crucial to complete the entire course of medication even if symptoms disappear early. Also, it’s important for all sexual partners to receive treatment to avoid re-infection.
3. What happens if chlamydia is left untreated?
If left untreated, chlamydia can cause serious health problems such as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in women. PID can lead to long-term pelvic pain and infertility due to damage to the fallopian tubes.
The infection can also spread and result in life-threatening complications like ectopic pregnancy. Therefore, prompt treatment is essential for avoiding these severe outcomes.
4. Who should get tested for chlamydia?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends annual screening for all sexually active women under 25 and older women with risk factors like new or multiple sex partners. Pregnant women should also get tested during their prenatal visits.
Men who have sex with men should consider regular screenings as well since they have higher risks of STIs like chlamydia. Regular screening ensures early detection and timely treatment.
5. How can I prevent getting chlamydia?
You can reduce your risk of getting chlamydia by using condoms consistently during vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Limiting your number of sexual partners and having open discussions about STI testing with them also help reduce risks.
Additionally, regular sexual health check-ups are important whether you exhibit symptoms or not. Early detection through routine screenings keeps you informed about your current health status.
Doctor explains SYMPTOMS of CHLAMYDIA in men and women
Conclusion
In understanding chlamydia, especially its symptoms like unusual discharge in women, early detection is critical. Regular screenings can identify the infection even when symptoms are absent. Timely treatment prevents severe health complications and ensures better overall sexual health.
Prevention strategies, such as using condoms and open communication with partners, are key to reducing the risk of chlamydia. Taking proactive steps in monitoring sexual health benefits both individuals and the broader community. Stay informed, get tested regularly, and prioritize your health.