A swollen thyroid, or goiter, can be a startling discovery, often rooted in dietary iodine deficiency. Contrary to common belief, it’s not always related to a malfunctioning gland but can be a benign anomaly, prevalent even sans obvious symptoms. This makes treatment approaches both challenging and varied.
Historical data reveals that before the advent of iodine fortification in the 20th century, goiters were overwhelmingly common in certain regions. Modern treatment options range from simple dietary supplements to more invasive procedures like thyroidectomy. Notably, a longitudinal study highlighted that iodine supplementation reduced goiter prevalence by nearly 90% over two decades.
Understanding Swollen Thyroid or Goiter
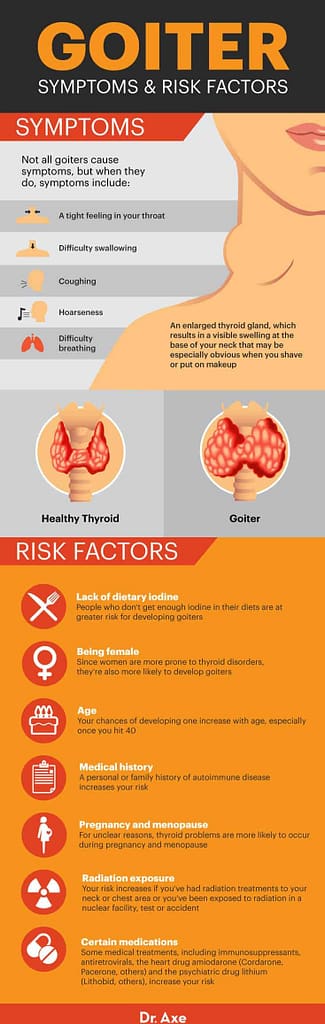
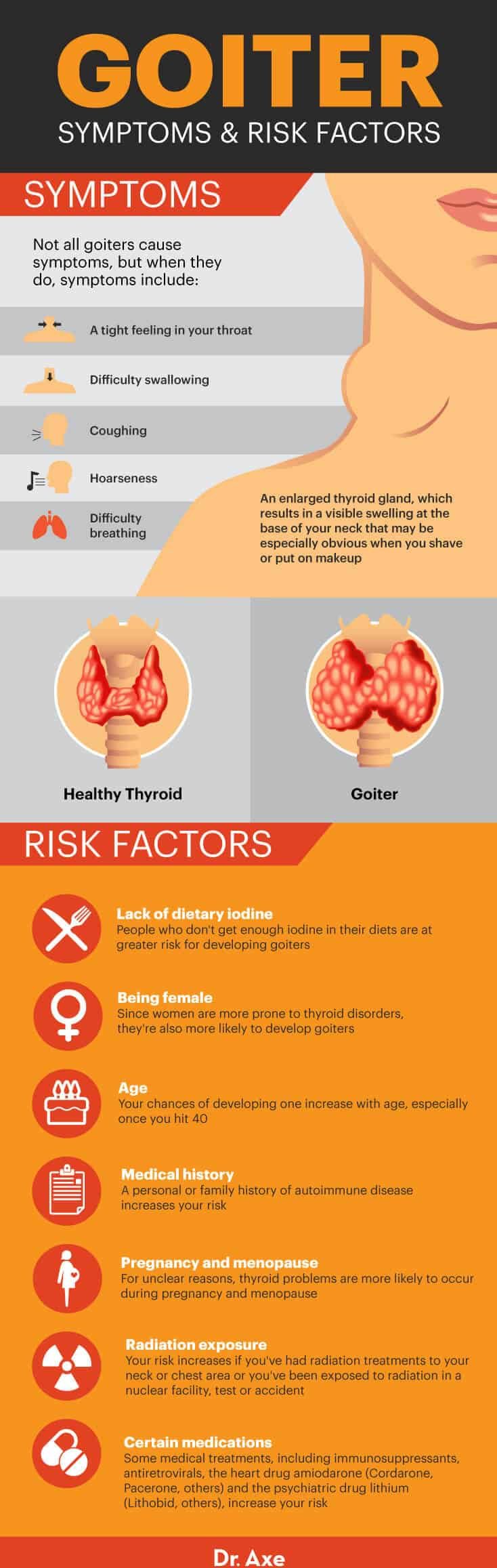
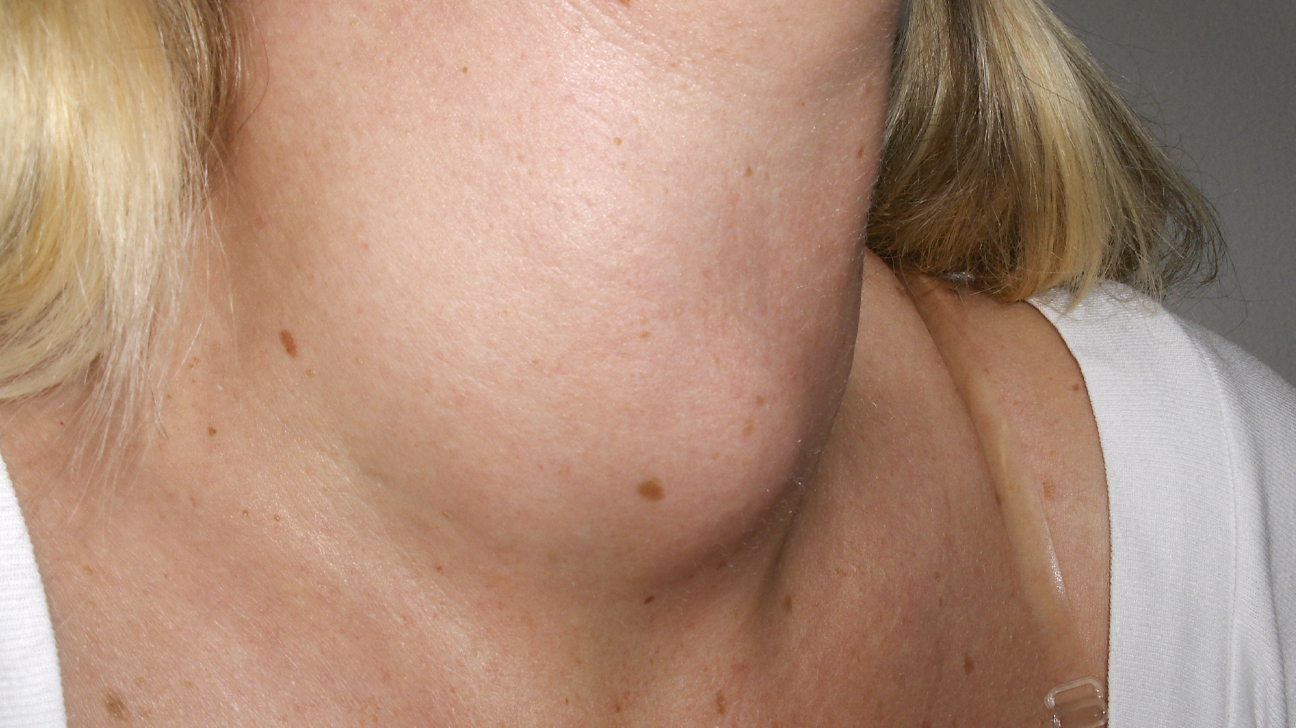
A **swollen thyroid**, also known as a **goiter**, is when the thyroid gland enlarges. Located in the neck, this gland produces hormones important for body functions. A goiter can happen in people of any age.
Goiters can be caused by various factors, including **iodine deficiency**, which is the most common cause worldwide. Other reasons can be autoimmune diseases like **Graves’ disease** or **Hashimoto’s thyroiditis**. Sometimes, nodules or lumps can also lead to a swollen thyroid.
Symptoms of a goiter can vary. Some people may have no symptoms, while others might experience a visible swelling, difficulty swallowing, or breathing problems. It’s essential to monitor these signs to avoid complications.
Diagnosing a Swollen Thyroid
Doctors use several methods to diagnose a swollen thyroid. A physical exam is often the first step, where the doctor feels the neck for swelling. They may also recommend blood tests to check thyroid hormone levels.
**Imaging tests** like ultrasounds or CT scans can provide a detailed view of the thyroid gland. These tests help in spotting nodules or other abnormalities. Sometimes, a biopsy might be needed to rule out cancer.
Causes of Goiter
**Iodine deficiency** remains a leading cause of goiter, especially in regions with low dietary iodine. Autoimmune disorders like Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis can also trigger thyroid enlargement. In some cases, genetic factors play a role.
Environmental factors, such as certain medications and radiation exposure, may contribute to goiter development. Hormonal changes during pregnancy and puberty can also affect thyroid size. Identifying the cause is crucial for effective treatment.
Symptoms and Complications
While many goiters are harmless, some can cause significant symptoms. These can include visible swelling, **difficulty swallowing**, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, the goiter can compress nearby structures, leading to complications.
Untreated goiters can lead to thyroid dysfunction, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Both conditions can impact overall health and quality of life. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can prevent these complications.
Swollen thyroid but blood test normal. What does it mean? – Dr. Harihara Murthy | Doctors’ Circle
Commonly Prescribed Medications for Swollen Thyroid Treatment
Treating a swollen thyroid often involves various medications. These drugs can help regulate thyroid hormone levels and reduce goiter size. Below are some key types of medications used.
Thyroid Hormone Replacement
**Levothyroxine** is a common medication prescribed to treat thyroid hormone deficiency. This synthetic hormone helps normalize thyroid levels and can reduce the size of the goiter. Patients typically take it as a daily pill.
The thyroid hormone replacement treatment aims to bring thyroid hormone levels back to normal. This can make goiters smaller over time. Regular monitoring and dose adjustments are essential.
Anti-Thyroid Medications
**Methimazole** and **propylthiouracil (PTU)** are anti-thyroid medicines. They work by preventing the thyroid gland from making too much hormone. These medications are often used in cases of hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid is overactive.
Anti-thyroid medications can help reduce symptoms like rapid heartbeat and anxiety. They are usually taken for several months. Doctors adjust dosages based on blood test results.
Iodine Supplements
In areas where iodine deficiency is common, supplements are often prescribed. **Iodine tablets** can help correct the deficiency and shrink the goiter. Iodized salt is another easy way to get enough iodine in your diet.
Ensuring enough iodine intake helps the thyroid function properly. It’s a simple yet effective way to manage mild goiters. Iodine supplements should be taken under medical guidance.
Role of Dietary Changes in Managing Swollen Thyroid
Diet plays a crucial role in managing a swollen thyroid. **Consuming adequate iodine** is essential for thyroid health. Foods like fish, dairy products, and iodized salt can help maintain proper iodine levels.
**Avoiding goitrogenic foods** can also be beneficial. Foods such as cabbage, broccoli, and soy contain compounds that may interfere with thyroid function. It’s advisable to limit their intake.
**Selenium** is another important nutrient for thyroid function. This mineral can be found in nuts, especially Brazil nuts, as well as in seeds and lean meats. Including these in your diet may support thyroid health.
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can also improve overall thyroid function. **Vitamins A, D, E, and B** are particularly important. A varied diet ensures you get these essential nutrients.
Surgical Solutions for Swollen Thyroid
For some patients, **surgery** becomes a necessary treatment for a swollen thyroid. Thyroid surgery is often recommended when a goiter causes breathing or swallowing difficulties. This procedure can also be a solution if there’s a suspicion of thyroid cancer.
The most common surgical option is a **thyroidectomy**. This involves either partial or complete removal of the thyroid gland. Partial thyroidectomy keeps some thyroid tissue intact, while a total thyroidectomy removes the entire gland.
A partial thyroidectomy might be selected if the goiter affects only part of the thyroid. This type of surgery has a quicker recovery time compared to a total thyroidectomy. However, some patients might still require hormone replacement therapy after the procedure.
**Total thyroidectomy** is more extensive and is required for more severe cases. This surgery removes the goiter entirely. Patients who undergo a total thyroidectomy will need to take lifelong thyroid hormone replacement.
Recovery after thyroid surgery usually involves a short hospital stay. Most patients can resume normal activities within one to two weeks. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial to monitor recovery and adjust any medications.
**Potential risks** of thyroid surgery include damage to vocal cords and parathyroid glands. These complications are rare but important to consider. Detailed discussions with a healthcare provider help weigh the benefits and risks.
Living with Swollen Thyroid: A Holistic Approach
Living with a swollen thyroid requires a **holistic approach** that goes beyond just medical treatments. This includes adopting lifestyle changes and mental health strategies. A comprehensive plan can help manage symptoms better.
**Regular exercise** is beneficial for overall health and thyroid function. Simple activities like walking or swimming can make a difference. Exercise boosts energy levels and supports a healthy metabolism.
- Yoga and meditation for stress relief
- Balanced diet rich in essential nutrients
- Adequate sleep for body recovery
Stress management is another crucial aspect. **Yoga and meditation** can help in reducing stress and improving well-being. Mindfulness practices have shown to positively impact thyroid health.
A balanced diet rich in **vitamins and minerals** aids in maintaining thyroid function. Foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and nuts are recommended. Ensuring sufficient iodine and selenium intake is vital.
Getting adequate sleep allows the body to heal and function optimally. Developing a consistent sleep routine enhances recovery and supports hormonal balance. Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night.
Frequently Asked Questions
Living with a swollen thyroid raises many questions. Here, we answer some common inquiries to help you understand the condition better.
1. What causes a swollen thyroid?
A swollen thyroid can be caused by several factors. The most common cause is iodine deficiency, which prevents the thyroid from functioning properly. Other causes include autoimmune diseases like Graves’ disease and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, which attack the thyroid gland.
Nodules or lumps in the thyroid can also cause swelling. Sometimes hormonal changes during pregnancy or puberty trigger goiter development. Environmental factors such as radiation exposure or certain medications may contribute too.
2. How is a swollen thyroid diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically starts with a physical exam where your doctor feels your neck for swelling. Blood tests are often conducted to check levels of thyroid hormones and antibodies.
Imaging tests like ultrasounds help visualize the gland and detect any abnormalities like nodules. In some cases, a biopsy may be needed to rule out cancer or other serious issues affecting the thyroid.
3. Can dietary changes improve thyroid health?
Yes, dietary changes can significantly improve thyroid health. Including iodine-rich foods like fish, dairy products, and iodized salt supports optimal gland function.
Avoiding goitrogenic foods such as cabbage and soy helps prevent interference with hormone production. Selenium-rich foods like nuts and seeds also promote healthy thyroid activity.
4. What medications are used to treat a swollen thyroid?
Your doctor may prescribe medications based on the underlying cause of your goiter. Levothyroxine is commonly used for hypothyroidism to normalize hormone levels and reduce swelling.
Methimazole or propylthiouracil (PTU) might be prescribed for hyperthyroidism as they inhibit excessive hormone production. Iodine supplements can also be beneficial in cases of deficiency-related goiters.
5. When is surgery necessary for treating a swollen thyroid?
Surgery might become necessary if the goiter causes severe symptoms like difficulty breathing or swallowing. It is also considered if there’s suspicion of cancer in the gland.
The most common procedure is a partial or total thyroidectomy where part or all of the gland is removed. Regular follow-ups post-surgery are crucial for monitoring recovery and managing hormone replacement therapy if needed.
Video: Natural ways to treat thyroid disease
Conclusion
Managing a swollen thyroid requires a comprehensive approach. From medical treatments and dietary changes to surgical options, each method has its unique benefits. Regular monitoring and a holistic lifestyle can greatly improve thyroid health.
Understanding the underlying causes and appropriate treatments is crucial for effective management. With proper care and expert guidance, living with a swollen thyroid becomes manageable. Prioritizing overall well-being will lead to a healthier life.