Underactive Thyroid Symptoms in Females: A Comprehensive Guide

The thyroid gland is that small, butterfly-shaped gland situated in the neck just below the larynx. It plays a significant role in regulating various functions of the body, such as metabolism, growth, and development. In females, an underactive thyroid, which is termed hypothyroidism, has several symptoms that can considerably affect everyday life. In this article, we will delve into common underactive thyroid symptoms in females and go on to look at the causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Common Underactive Thyroid Symptoms in Females
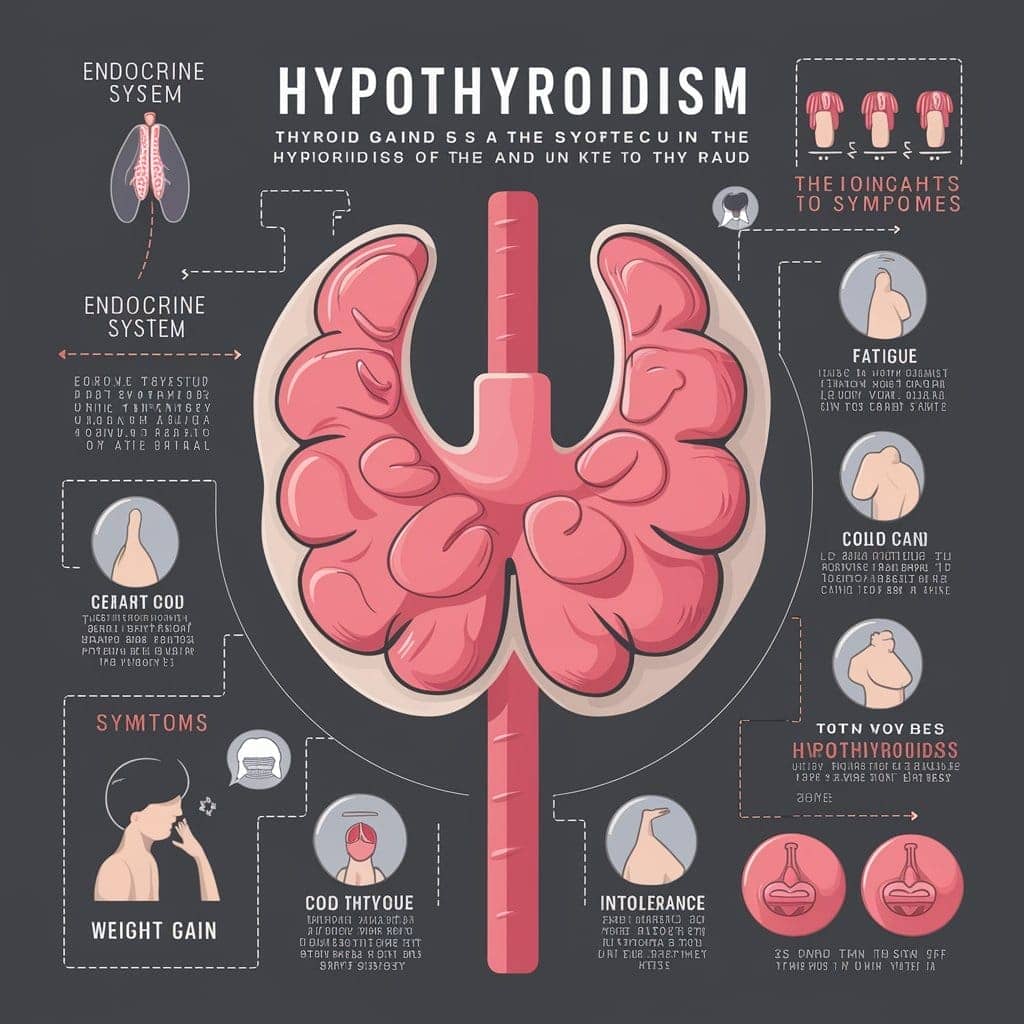
Common symptoms of hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) in females include:
- Fatigue and Weakness: Feeling tired, sluggish, and lacking energy are common symptoms of hypothyroidism in females. This can make it difficult to perform daily tasks, exercise, or even get out of bed.
- Weight Gain: Unexplained weight gain, particularly in the midsection, is a common symptom of hypothyroidism. This can lead to feelings of self-consciousness and low self-esteem.
- Hair Loss: Thinning or falling hair, particularly on the scalp, eyebrows, and pubic area, can be a distressing symptom of hypothyroidism in females.
- Dry Skin: Dry, rough, and itchy skin can be a sign of hypothyroidism. This can lead to skin conditions like eczema and acne.
- Cold Intolerance: Feeling cold even in mild temperatures, or having cold hands and feet, can be a symptom of hypothyroidism.
- Memory Problems: Difficulty concentrating, memory lapses, and forgetfulness can occur due to hypothyroidism.
- Mood Changes: Depression, anxiety, and mood swings are common symptoms of hypothyroidism in females.
- Heavy or Irregular Periods: Hypothyroidism can cause heavy, irregular, or prolonged menstrual periods, leading to anemia and other complications.
- Infertility: Hypothyroidism can affect ovulation and fertility, making it difficult to conceive.
- Muscle and Joint Pain: Pain and stiffness in the muscles and joints, particularly in the neck, shoulders, and hips, can occur due to hypothyroidism.
- Constipation: Slowed digestion and constipation can be symptoms of hypothyroidism.
- Swollen Feet and Ankles: Fluid retention can cause swelling in the feet and ankles, leading to discomfort and pain.
Causes of Hypothyroidism in Females
- Autoimmune Thyroiditis: The most common cause of hypothyroidism, is when the immune system attacks the thyroid gland.
- Thyroid Surgery: Removal of part or all of the thyroid gland can lead to hypothyroidism.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation to the neck can damage the thyroid gland, leading to hypothyroidism.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can cause hypothyroidism.
- Pituitary Gland Problems: The pituitary gland regulates thyroid hormone production. Problems with the pituitary gland can lead to hypothyroidism.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, including:
- Thyroid Function Tests: Blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels, including TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), T4, and T3.
- Thyroid Ultrasound: An imaging test to examine the thyroid gland.
The treatment typically involves replacement therapy with thyroid hormones, which are synthetic hormones taken to replace those that the thyroid is not producing. The main objective is to have normal thyroid hormone levels again in order to remove the symptoms.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Hypothyroidism
- Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc can help support thyroid function.
- Exercise: Regular exercise, such as yoga and walking, can help improve mood and energy levels.
- Stress Management: Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, can help manage symptoms.
- Sleep: Getting adequate sleep is essential for overall health and thyroid function.
What are the risk factors for developing hypothyroidism?
Here are the risk factors for developing hypothyroidism in females:
1. Age: The risk of hypothyroidism increases with age, particularly after menopause. Women over 50 are more likely to develop hypothyroidism.
2. Family History: Having a family history of thyroid disease, particularly hypothyroidism, increases the risk of developing the condition.
3. Autoimmune Disorders: Women with autoimmune disorders, such as type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or lupus, are at a higher risk of developing hypothyroidism.
4. Thyroid Surgery or Radiation: Women who have had thyroid surgery or radiation therapy to the neck are at risk of developing hypothyroidism.
5. Pregnancy and Postpartum: Women who have had multiple pregnancies or have experienced pregnancy-related complications, such as preeclampsia, are at a higher risk of developing hypothyroidism. Postpartum thyroiditis, a condition that occurs in the first year after childbirth, can also increase the risk of hypothyroidism.
6. Iodine Deficiency: Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production. Women who live in areas with iodine-deficient soil or have a diet that is severely lacking in iodine are at risk of developing hypothyroidism.
7. Radiation Exposure: Radiation exposure, such as from radiation therapy or nuclear fallout, can increase the risk of hypothyroidism.
8. Certain Medications: Taking certain medications, such as lithium, can increase the risk of hypothyroidism.
9. Pituitary Gland Problems: Women with pituitary gland problems, such as a pituitary tumor, can develop hypothyroidism.
10. Vitamin D Deficiency: Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of hypothyroidism.
11. Menopause: Women going through menopause are at a higher risk of developing hypothyroidism due to hormonal changes.
12. Obesity: Women who are obese or have a body mass index (BMI) over 30 are at a higher risk of developing hypothyroidism.
13. Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of hypothyroidism.
14. Previous Thyroid Problems: Women who have had previous thyroid problems, such as thyroid nodules or goiter, are at a higher risk of developing hypothyroidism.
15. Genetic Mutations: Certain genetic mutations, such as those associated with Turner syndrome or Down syndrome, can increase the risk of hypothyroidism.
Conclusion
Hypothyroidism can seriously impact a woman’s quality of life but properly diagnosed and treated, it can be controlled to improve her general health. Knowing the common symptoms, causes, and treatment possibilities, women can be in control of their health and can seek medical help when they notice any of the above-listed symptoms. Remember, it’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses individual needs and health goals.