Thyroid problems, mainly hypothyroidism, happen more frequently in women than men and can have a great effect on general health. Early signs of the disease must be identified promptly for correct treatment. This article examines some early indications of thyroid problems in women, why they are not easily noticed at times, and the significance of learning about these diseases and their management.
Key Takeaways
- The incidence of hypothyroidism is higher among women, affecting them 8-9 times more than men, necessitating awareness and screening in women’s health care.
- Due to its subtle signs that can easily be misdiagnosed or go unnoticed, early detection of hypothyroidism is crucial.
- In addition to metabolism, the impacts of hypothyroidism on women include profound effects on reproductive health and emotional well-being.
- It is important to seek medical help when you notice symptoms such as a general slowing down of the body functions because it may take years before one realizes they have hypothyroidism.
- Preventive strategies and long-term management of thyroid health include lifestyle changes, nutritional aspects, and regular thyroid function tests.
Understanding Hypothyroidism and Its Prevalence in Women
The Role of the Thyroid Gland
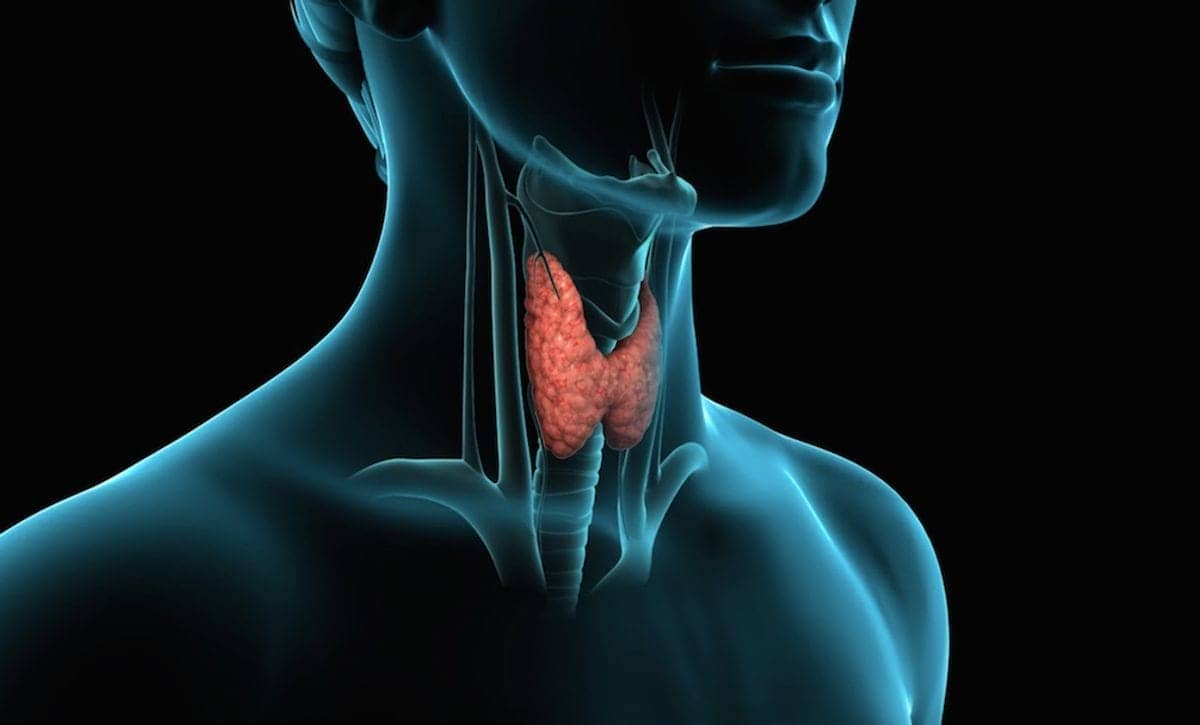
The thyroid gland, a small butterfly-shaped organ located at the base of the neck, is fundamental to our body’s metabolism and energy regulation. They synthesize two key hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), important for physiological processes. They enable control of heart function, body metabolic rate, mood, and digestion.
The production as well as release of thyroid hormones is regulated by the pituitary gland via the secretion of Thyroid–stimulating hormone (TSH). The TSH signals the thyroid to produce and release T3 and T4. It is synonymous with what takes place between a thermostat that controls the temperature in a house and an entire heating system; the Pituitary gland adjusts the levels of TSH to maintain equilibrium in the internal environment.
Proper working is very important to ensure overall health, and any imbalance in hormone production can lead to serious health complications.
The role of the thyroid gland extends far beyond these primary functions. It also influences the body’s growth, temperature regulation, and even fertility. Women, in particular, may experience changes in their menstrual cycle and ovulation due to thyroid imbalances, thus elucidating the gland’s importance in reproductive health.
Comparative Incidence in Men and Women
The thyroid gland disorders of the thyroid gland have characteristic presentations according to gender; however, women are more prone to certain diseases. They have about six times a higher risk for developing thyroid nodules and about three times a higher risk for developing thyroid cancer compared to men. Some of this difference is because nodular growth is more sensitive to estrogen, which is more common in women.
The risk of malignancy in thyroid nodules increases after menopause or in men, and notably, thyroid nodules in children carry a significant risk, with a 50% likelihood of being malignant.
Understanding the gender-specific prevalence of thyroid issues is crucial for the targeted prevention and treatment strategies.
Here is a brief overview of the comparative incidence:
- Estrogen sensitivity leads to higher nodule development in women.
- Post-menopausal women and men with nodules face a greater risk of malignancy.
- Children with thyroid nodules have a high risk of cancer, necessitating careful medical evaluation.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of hypothyroidism helps to prevent its progression and minimize any health complications that may arise. Early recognition can greatly enhance the quality of life for women, allowing for earlier intervention and management. Without prompt attention, hypothyroidism might worsen into more severe symptoms and impact overall health.
- Early Symptoms: Fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and menstrual irregularities.
- Health Risks: If left untreated, can result in heart problems, infertility, and mental health issues.
- Management: Early detection enables better disease management through medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring.
Recognizing the early signs of thyroid issues is not just about addressing the immediate symptoms; it’s about taking proactive steps to maintain long-term health and well-being.
Identifying the Early Signs of Hypothyroidism
Common Symptoms to Watch For
When considering early warning signs of thyroid problems in females, it’s essential to recognize the variety of symptoms that can manifest. Hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland is underactive, often presents with signs that are easily mistaken for other health issues, making early detection challenging.
- Fatigue and a general feeling of lethargy
- Unexplained weight gain
- Sensitivity to cold temperatures
- Dry skin and hair
- Menstrual irregularities
- Constipation
- Muscle weakness and joint pain
These symptoms may appear gradually and can be subtle, which is why they are frequently overlooked. However, acknowledging these changes is crucial for timely intervention.
Persistent symptoms, especially when they occur in combination, should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider. While each symptom on its own may not be alarming, the collective presence of several can indicate the need for a thyroid function evaluation.
Why Symptoms Are Often Overlooked
The symptoms of hypothyroidism are often subtle and can be mistaken for the normal ebbs and flows of life. Fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance are common complaints that might not immediately raise red flags for thyroid issues. These symptoms can easily be attributed to a busy lifestyle, stress, or aging, leading many to dismiss them without considering a thyroid evaluation.
- Fatigue and weakness
- Weight changes
- Cold intolerance
- Cognitive impairment
The nonspecific nature of these symptoms means they can overlap with a variety of other conditions, making it challenging to pinpoint hypothyroidism as the culprit. For instance, unexplained weight changes could be due to hormonal imbalances, dietary factors, or other health concerns. Persistent pain or cognitive issues like brain fog and lack of concentration are often misdiagnosed or overlooked entirely.
It is crucial to listen to your body and take note of persistent or worsening symptoms. While they may seem minor, they could be indicative of an underlying thyroid problem that requires medical attention.
The Significance of Subtle Changes
The early signs of hypothyroidism in women can be deceptively mild, yet they hold significant health implications. Subtle changes, when overlooked, can progress to more severe conditions, making it imperative to pay attention to even the smallest shifts in one’s well-being.
- Unexplained Weight Changes: Sudden weight gain or loss may indicate thyroid issues.
- Hair Loss and Texture Changes: Thinning hair, especially at the eyebrows’ outer edge, and changes in hair texture are common signs.
- Persistent Fatigue: A relentless feeling of tiredness that rest doesn’t alleviate could be a symptom.
-
Mood and Mental Health: Depression and anxiety are frequently present in the course of thyroid disorders. Approximately 20% of women with hypothyroidism will develop depression and as many as 30-40% of those with hyperthyroidism experience anxiety symptoms. The association of thyroid dysfunction with mood disorders becomes well established when a study, using 500 patients, is considered.
These are early signs to keep an eye out for, no matter how unimportant they may seem individually. Together, they can paint a better picture of thyroid health. Keep a record of the changes and discuss with your healthcare provider for proper assessment and timely intervention.
The Impact of Hypothyroidism on Women’s Health
Metabolic Changes and Weight Management
Hypothyroidism can cause huge metabolic changes, often resulting in weight gain. This is due to a slowed metabolism, which reduces the body’s capability to burn energy effectively. Even with a careful food plan and exercise, weight management may be an undertaking for people with an underactive thyroid.
Nutrition and calorie intake play an essential function in thyroid function. A weight loss plan that helps thyroid health is important for dealing with signs and retaining a wholesome weight. For instance, a low-glycemic load weight loss plan may also positively impact thyroid characteristic assessments in people with an ordinary Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Thyroid axis.
Lifestyle adjustments, In managing hypothyroidism-related weight changes, lifestyle adjustments, mainly balanced diets and regular exercise, have been important. Indeed, the adjustments may need customization for each person since, as in all kinds of conditions, the illness affects people differently.
Unexplained weight changes should not be overlooked, as they could indicate an underlying thyroid issue. If you experience unexpected weight gain or loss, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and management.
Reproductive Health Concerns
Hypothyroidism may also have repercussions on a woman’s reproductive system. Thyroid hormones are crucial in the regulation of an ideal menstrual cycle, and imbalances can be responsible for the irregularity of these periods or even for amenorrhea, or the lack of menses.
In women with hypothyroidism, fertility difficulties may be associated with thyroid function since ovulation has been discovered to be very important.
Here are some key points about the relationship between thyroid health and reproductive outcomes.
- Thyroid hormones regulate the menstrual cycle and support ovulation.
- Hypothyroidism can lead to heavier, more frequent, or irregular menstrual bleeding.
- Suboptimal thyroid function may reduce fertility and increase the risk of miscarriage.
Timely diagnosis and governance of thyroid diseases could bring about healthier reproductive systems for women, which, in turn, could help in producing the proper reproductive health results for women. There is regular assessment of thyroid function, which is mainly helpful to pregnant women or those who are seeking to become pregnant and then all in questions about issues relating to reproductive health.
Women may additionally visit their healthcare provider to locate a terrific treatment and management method to assist restore balance and improve the overall reproductive fitness of the sufferers suffering from thyroid-related demanding situations.
Psychological and Emotional Well-being
The thyroid gland has a special function in the control of moods and maintaining emotional stability. Hypothyroidism is likely to give rise to some psychological conditions that do not include depression and anxiety. At the very beginning, the indications may be so faint, but then these can become very severe if left unattended.
The presence of mood alternation, for instance, lengthy-lasting unhappiness and an experience of emptiness, in human beings with “hypothyroid” is an ordinary element to manifest. Identifying those emotional symptoms as arguments of thyroid trouble needs to be emphasized as opposed to writing them off as pressure scattered or the result of being older.
Psychological implications that can arise from hypothyroidism include mental health troubles, interpersonal relations, and performing daily routines. Below are some key emotional symptoms associated with hypothyroidism:
- Anxiety or increased nervousness
- Irritability or mood swings
- Difficulty concentrating or memory problems
While these symptoms may indicate hypothyroidism, they also often appear in other medical disorders. Discussion with a medical professional is important for identification and treatment.
When and How to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing the Need for a Healthcare Provider
It is important to listen to your body and be alert to any signs that may point to a thyroid problem. If the symptoms persist for a long time, that is, with fatigue, weight, and mood changes, this is the best time to see a healthcare professional.
Below are some of the steps that will help you discern when to seek medical attention:
- Monitor your symptoms and their frequency.
- Note any changes in your energy levels, appetite, or mood.
- Keep track of your menstrual cycle for any irregularities.
- Be aware of any family history of thyroid disease.
While some of the symptoms may seem minor, they may be early indicators of a thyroid condition. Better the earlier sign, with professional counsel, to diagnose and treat the condition.
Finding the right healthcare provider is important. Choose an endocrinologist or a practitioner who has experience with thyroid disorders. They will be able to run a comprehensive evaluation, which will include a physical, bloodwork, and possibly an ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
What to Expect During the Diagnosis Process
When you go to your healthcare provider with issues that are troubling about the function of the thyroid, you should expect a full evaluation. This would include a thorough medical history and physical examination with your doctor.
They will be checking for physical signs of hypothyroidism, including a swollen thyroid gland or slow heart rate. Afterward, specific tests are ordered to measure thyroid hormone levels. The most common tests include: the TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) test
- Free T4 test
- Free T3 test
- Thyroid antibody tests
These help determine if your thyroid is underactive and to what extent. Note, however, that normal ranges do vary; interpretation of results should be done by a healthcare professional.
If the test shows you to have a deficient thyroid hormone level, then your doctor will discuss the best course of action for you. This may include synthetic hormone replacement therapy and regular checks on your thyroid function
Remember, every patient’s experience with diagnosis may differ; therefore, additional tests may be necessary to rule out other conditions. So, make sure to keep an open line of communication with your healthcare provider at all times.
Choosing the Right Specialist for Thyroid Issues
After realizing the need for professional medical advice regarding thyroid issues, it is important to choose the right specialist. An endocrinologist is a physician who specializes in hormonal disorders, including those of the thyroid gland.
While a general physician may be able to manage most hypothyroidisms, especially in their early stages, an endocrinologist may be recommended in more advanced or complex cases.
It is important that one can find a healthcare provider who would know the expertise and get it more to your specific health condition and worries.
Here are some factors to consider when choosing a specialist:
- Experience and expertise in thyroid disorders
- Accessibility and availability for consultations
- Communication style and willingness to answer questions
- Patient reviews and testimonials
Remember, overcoming thyroid disease with the right treatment plan is very important to your well-being. Don’t hesitate to seek advice from ENT doctors or consult with an endocrinologist who can bring comprehensive care and support throughout your treatment journey.
Prevention and Management Strategies for Thyroid Health
Lifestyle Adjustments and Nutritional Considerations
Positively addressing healthy lifestyle issues is necessary to ensure the control of thyroid disorders. Regulating exercise is much more advanced compared to some of the other types mentioned; rather, it promotes heart health and the body’s muscles. Eating a balanced diet that includes the recommended amount of all vital nutrients is a must for this condition.
Nutrients that are particularly important for thyroid health include:
- Iodine: is crucial for the production of thyroid hormones.
- Selenium: Helps protect the thyroid gland from oxidative stress.
- Zinc: is essential for the conversion of thyroid hormones to their active form.
while lifestyle changes are important, they may not always be sufficient on their own. You ought to recognize when additional medical intervention is needed.
Remember, each individual’s needs may be different, and it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for a fitting plan.
Understanding Thyroid Function Tests
The blood analysis range on thyroid function is a fundamental principle used in thyroid detection and treatment. These tests determine the concentration of thyroid hormones in the blood samples.
Thus, thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), triiodothyronine (T3), and thyroxine (T4) are among the main indicators. Hormone level imbalance may manifest itself either as hyper or hypothyroidism, the conditions that are characterized by hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) or hyperthyroidism (underactive thyroid).
Thyroid function tests are not only diagnostic but also help in monitoring the effectiveness of treatment over time.
Continuous measuring of the levels of thyroid hormones becomes the most important because even the existing patients with thyroid problems should have their hormone levels checked. The frequency of testing may become less, for some patients, when they do a self-test once every six to twelve months. It’s critical to follow your thyroid specialist’s advice to do checkups on time to make sure your thyroid is in good condition.
Having good viewpoints about the outcomes of thyroid function tests is one of the keys to thyroid health management. Here’s a simple breakdown of what each test indicates: Here’s a simple breakdown of what each test indicates:
- TSH: Indicates overall thyroid function.
- T3 and T4: Measure the levels of active thyroid hormones.
- Thyroid Antibodies: Help identify autoimmune thyroid conditions.
Long-term Management of Hypothyroidism
Constant blood tests are critical for monitoring thyroid activity and therefore making adjustments to the drugs when this is necessary. Usually, these laboratory tests involve recording levels of a specific protein known as thyroglobulin that can be an indication of the activity of thyroid tissue either in cancer recurrence or as a marker.
Upon proper management of thyroid health through healthy habits and understanding about thyroid health, individuals can optimize treatment outcomes and improve the quality of life.
Cost considerations should also be taken into account, as the price of medication can vary. Generic prescriptions may offer a more cost-effective option compared to name-brand drugs. Always discuss with your healthcare provider or pharmacist for the most suitable and affordable treatment options.
Conclusion
In conclusion, early warning signs of thyroid problems in females can be subtle, so it’s important to listen to your body. Fatigue, unexpected weight changes, mood swings, and changes in your menstrual cycle are common red flags. Additionally, feeling unusually hot or cold, hair loss or dry skin can be signs of a thyroid issue. If you notice any of these symptoms, consult your doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing thyroid disorders.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1. What is hypothyroidism, and why is it more prevalent in women?
Hypothyroidism is a medical condition manifested by the thyroid gland’s underproduction of vital hormones which in turn affects the body’s metabolism and energy production. It is twice as common in women, even though the prevalence in men is about 1 out of 10, while in women, it is as high as 9 out of 10. The reasons for this inequality vary among the experts and may include hormonal differences and autoimmune factors.
Q.2. What are the early signs of hypothyroidism in women that should not be ignored?
Early signs of hypothyroidism in women include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, dry skin, thinning hair, and menstrual irregularities. It’s important to pay attention to these subtle changes as they can be easily overlooked.
Q.3. Why are the symptoms of hypothyroidism often overlooked?
The symptoms of hypothyroidism can be multiple and mimic other conditions, making it easy to dismiss or attribute them to stress, aging, or lifestyle factors. Moreover, symptoms often develop slowly, making them unnoticeable.
Q.4. How can hypothyroidism impact a woman’s reproductive health?
Hypothyroidism can lead to menstrual irregularities and complications during pregnancy, not to mention fertility issues. It is therefore very imperative for women to monitor their health related to their thyroid during times of trying to conceive or experiencing reproductive health concerns.
Q.5. When should a woman seek medical attention for potential thyroid issues?
a woman experiences symptoms like unexplained fatigue, weight changes, or menstrual irregularities, or if hypothyroidism runs in her family, she needs to seek medical help. Early detection can lead to better management of the condition through a healthcare provider.