Exploring the Causes of Rust-Colored Stains on Hands Overnight

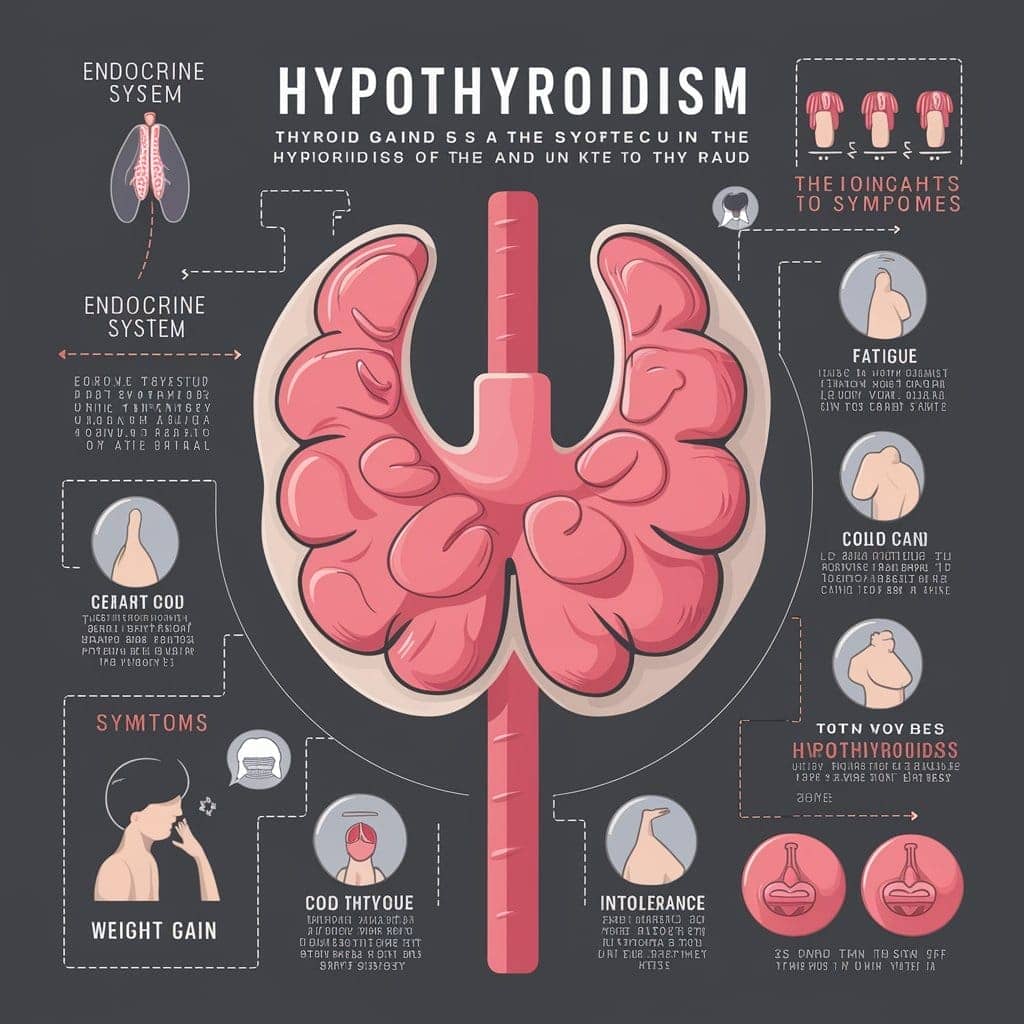
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disorder that is quite common and one of the most prevalent in the population. It is characterized by a deficiency of thyroid hormones, which may manifest in a wide range of symptoms, including those related to the skin. It has been documented that some patients express rusty skin marks on their hands after a night’s sleep.
The present article reviews and assesses the possible connection between hypothyroidism and skin manifestations evaluates the diagnostic procedure, and discusses the management of this condition along with its dermatological problems.
What Is Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a medical condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones for your body’s requirements. Various bodily functions, such as metabolism, energy levels, and skin health, are controlled by the thyroid gland.
Why does hypothyroidism affect your hands?
Hypothyroidism is when your thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. This hormone is very important in controlling metabolism, which controls many functions of the body. Here is how a slow metabolism due to hypothyroidism can lead to issues with your hands:
-
-
-
- Fluid Retention: Hypothyroidism may result in the buildup of fluid in tissues, especially those in your hands, thus leading to the development of swelling and puffiness.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS): The reduced function of thyroid hormones that occurs in hypothyroidism is actually unloading fluid into the body. This can put pressure on the median nerve, which runs down your arm into the hand. This can therefore cause tingling, numbness, and pain in your fingers, leading to symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Skin Changes: A slowed metabolism may result in the appearance of dry, rough, and flaky skin. Your palms may develop a yellowish tint. The nails will turn brittle and sluggish in their growth.
- Joint and Muscle Pain: Hypothyroidism can cause joint stiffness, aches, and muscle pain, which can include pain in your hands.
- Cold Sensitivity: Your hands may feel cold even in moderate weather, and low levels of thyroid hormone can increase your sensitivity to cold temperatures.
-
-
Key Takeaways
- Hypothyroidism can cause a range of skin changes, including the rare occurrence of rust-colored stains on hands, which may appear suddenly.
- Hormonal imbalances in hypothyroidism affect skin health, potentially leading to unusual skin manifestations that warrant further medical investigation.
- Diagnosing hypothyroidism involves a combination of thyroid function tests and dermatological examinations to confirm the cause of skin discoloration.
- Treatment for hypothyroidism typically includes thyroid hormone replacement therapy, which may also alleviate associated skin symptoms over time.
- Patient education is crucial for managing expectations regarding the prognosis of skin changes and for providing support through resources and long-term care.
Exploring the Link Between Hypothyroidism and Skin Changes
Understanding Hypothyroidism and Its Symptoms
Hypothyroidism is a condition characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, which leads to a deficiency in thyroid hormones. These hormones are crucial for regulating metabolism, and their shortage can cause various symptoms. The most common signs of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and dry skin.
On the contrary, hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are opposite conditions. In hyperthyroidism, there is an active, functioning thyroid gland, leading to an excess of thyroid hormones. This may cause symptoms like weight loss, anxiety, heat intolerance, and sweating.
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Dry skin
- Muscle weakness
- Constipation
Early detection and treatment of hypothyroidism are essential to prevent complications. While symptoms may develop slowly, they can lead to serious health consequences if not treated promptly. It is a priority for people who experience such symptoms to get advice from a healthcare provider.
The Impact of Hormonal Imbalance on Skin
Hormonal imbalances, particularly those involving the thyroid hormone, can lead to a variety of skin changes. Hypothyroidism can cause the skin to become dry, thick, and pale, which may be accompanied by a coarse and scaly texture. The reduced thyroid function slows down the metabolism, which in turn can decrease sweating and result in drier skin.
- Dryness and flakiness
- Pale or yellowish complexion
- Coarse, scaly texture
- Puffiness, particularly around the eyes
- Delayed wound healing
The skin is a reflection of our internal health, and changes in its appearance can be one of the first signs of a thyroid disorder.
it is important to Any sudden or progressive change in the skin may mean an underlying health issue, so it’s important to pay attention. In the case of hypothyroidism, the dermatological examination, along with the tests for thyroid function, can aid in diagnosing both conditions.
Case Studies: Unusual Skin Manifestations in Hypothyroid Patients
Hypothyroidism may have a wide variety of skin manifestations that often go unrecognized, unmentioned, or misdiagnosed due to their scarcity or subtlety. Several case studies have manifested such altered skin features as those of hypothyroid patients who had not been diagnosed. They can range from dry, coarse skin to more peculiar signs like myxedema or carotenemia, which can give the skin a yellowish appearance.
- The patient experienced thickening of the skin, particularly on the shins, which was initially mistaken for dermatitis.
- Patient B reported hives that would not respond to typical antihistamine treatment.
- Patient C noticed a gradual yellowing of the skin, later linked to the decreased metabolism of carotene.
In each case, the skin changes were a clue to the underlying thyroid dysfunction, emphasizing the importance of a thorough clinical evaluation. The resolution of skin symptoms often paralleled the treatment of the thyroid condition, underscoring the skin’s sensitivity to hormonal levels.
Their anecdotal experiences point to the consideration of thyroid function tests in cases of atypical skin presentations, especially those that don’t fit with common diagnoses of dermatology.
The Mystery of Rust-Colored Stains on Hands
An Overview of Skin Discoloration Causes
Skin discoloration can manifest in various forms and can be indicative of numerous underlying health conditions. Rust-colored stains on the hands, specifically, may raise concerns due to their sudden appearance and unusual hue.
Skin discoloration can be attributed to a wide range of causes, whether external or derived from an internal disease.
- External Factors: Exposure to certain chemicals, dyes, or metals.
- Infections: Bacterial, fungal, or viral infections that affect skin pigmentation.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Dermatitis, psoriasis, or eczema can lead to changes in skin color.
- Systemic Diseases: Conditions like Addison’s disease, liver disease, and hypothyroidism.
It is essential to consider the patient’s overall health, recent activities, and any other symptoms they may be experiencing when evaluating skin discoloration.
A thorough medical history and physical examination are crucial in narrowing down the potential causes and determining the appropriate diagnostic tests. The sudden appearance of rust-colored stains on the hands overnight is particularly unusual and warrants a detailed investigation to rule out serious conditions.
Analyzing Overnight Changes in Skin Appearance
When rusty-colored stains appear on the hands overnight, such concerns can be both scary and perplexing. The onset of such discoloration usually foretells an underlying condition, and various factors can result in these changes, such as exposure to the environment, contact with staining substances, or even internal physiological processes.
- Environmental factors such as metals or chemicals
- Contact with staining substances like dyes or foods
- Internal conditions, including liver disease, hemochromatosis, or hypothyroidism
It is crucial to consider the broader context of the individual’s health when assessing sudden skin changes. A comprehensive approach that looks at recent activities, potential exposures, and existing health conditions is essential for accurate diagnosis.
This change in the skin can take place in cases of hypothyroidism, especially when there’s reduced metabolism and altered circulation. Such alterations can be obvious; one may notice dryness and pallor of the skin, along with even darker stains and rust in appearance. Such changes do not point towards any literal evidence of hypothyroidism, but with other symptoms and signs that seem indicative of such cases, further medical investigations are warranted.
Differential Diagnosis: When to Suspect Hypothyroidism
When patients present with rust-colored stains on their hands that have appeared overnight, clinicians should consider a differential diagnosis that includes various conditions. Hypothyroidism should be suspected when this skin change is accompanied by other symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance.
- Unexplained skin changes
- Presence of additional hypothyroid symptoms
- Recent changes in medication or diet
- Family history of thyroid disorders
It is crucial to take a thorough patient history and perform a physical examination to rule out other causes of skin discoloration before attributing it to hypothyroidism.
A timely diagnosis is essential for managing the condition effectively and preventing further complications. If hypothyroidism is suspected, the next steps include specific thyroid function tests and a dermatological assessment to confirm the diagnosis and understand the extent of skin involvement.
Key Tests for Detecting Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is diagnosed primarily based on blood test results showing thyroid hormone levels and TSH. The most definitive test is the TSH assay, which evaluates how well the thyroid gland functions.
- TSH Test: Measures the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood.
- Free T4 Test: Assesses the amount of free thyroxine, the primary hormone produced by the thyroid gland.
- Free T3 Test: Sometimes ordered to check the level of triiodothyronine, another thyroid hormone.
- Thyroid Antibody Test: Determines the presence of antibodies against thyroid peroxidase (TPO) and thyroglobulin, which can indicate autoimmune thyroid disease.
Early detection and accurate diagnosis are crucial for managing hypothyroidism effectively. These tests help in identifying the condition and guiding the appropriate treatment.
It’s important for patients to understand that while these tests are essential, they are part of a comprehensive evaluation that includes a physical examination and a review of symptoms and medical history.
Interpreting Thyroid Function Test Results
Understanding the results: It is most critical to note that these are tests undertaken to study the secretion of the levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine (T4), which will help in confirming hypothyroidism. In patients with hypothyroidism, normal levels of TSH and low levels of T4 almost always point to such an abnormality.
Here’s a simple guide to the key thyroid function tests and what their results might suggest:
- TSH Test: Measures how much TSH is in the blood. A high TSH level often signals an underactive thyroid.
- Free T4 Test: Measures the free, unbound thyroxine levels in the blood. Low levels can point to hypothyroidism.
- Total T4 Test: Measures the total amount of T4, including the portion that is bound to proteins in the blood. It can be affected by protein levels and might not be as accurate as the Free T4 Test.
- A free T3 test is sometimes ordered if T4 levels are normal but a patient still has symptoms of hypothyroidism. It measures the active thyroid hormone, triiodothyronine.
It’s important to consider that some medications and conditions can affect test results, making interpretation complex. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is necessary to accurately diagnose thyroid conditions.
Interpreting these results in the context of clinical symptoms and other laboratory findings is essential for an accurate diagnosis. A single abnormal result may not be sufficient for diagnosis; trends in hormone levels over time are often more telling.
The Role of Dermatological Examination in Thyroid Disorders
A dermatological examination may pivot in diagnosing the etiology of thyroid disorders, viz., hypothyroidism. Skin changes are often the first signs of hormonal imbalances and may prompt further investigations into thyroid function.
- Visual inspection of the skin, hair, and nails for abnormalities
- Palpation of the skin to assess texture and moisture
- Noting any presence of unusual stains or discolorations
Dermatologists can identify minor skin changes that indicate underlying thyroid issues. Their skills are needed to guide accurate laboratory tests and imaging studies for a definitive diagnosis.
The findings from a dermatological examination can complement blood tests and imaging results, providing a comprehensive picture of the patient’s health. It is important for patients to understand that skin manifestations may improve with proper thyroid treatment, but this is a gradual process and requires patience and consistent care.
Treatment Strategies for Hypothyroidism and Skin Complications

Conventional Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy
Replacement with synthetic thyroid hormones, predominantly levothyroxine, is an all-around approach to the management of hypothyroidism; they are used to replace the deficit hormones and rectify metabolism.
Patients usually commence with a low dose of medication, followed by gradual increases according to response to the therapy and thyroid function tests. The understanding among patients that this therapy is usually a lifetime commitment and requires constant monitoring can’t be overemphasized.
Consistency of taking the medication at the same time every day and careful avoidance of certain foods or other supplements interacting with absorption are important for effectiveness in treatment.
The following table outlines the key aspects of thyroid hormone replacement therapy:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Medication | Levothyroxine (Synthetic T4) |
| Dosage | Individualized based on weight, age, and thyroid function tests |
| Administration | Oral, typically in the morning on an empty stomach |
| Monitoring | Regular thyroid function tests to adjust dosage |
| Interactions | Certain foods and medications can affect hormone absorption |
As long as patients adhere to their prescribed therapy and open up communication lines to their healthcare providers, they can effectively manage their hypothyroidism and avoid its impact on the skin.
Addressing Skin Symptoms: Topical and Systemic Treatments
Accordingly, skin symptoms associated with hypothyroidism are usually handled by means of a combined topical and systemic treatment. Topical treatments alleviate symptoms such as dryness, itchiness, and discoloration and may involve prescriptions for moisturizers and steroid creams.
Systemic treatments, on the other hand, address the underlying hormonal imbalance. These may involve:
- Thyroid hormone replacement therapy
- Adjustments to existing medication regimens
- Nutritional supplements to support skin health
Patients must realize that despite giving symptomatic alleviation, systemic treatments are called for to remedy the root cause of skin changes; hence topical treatments should be supported by systemic treatments.
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure monitoring of treatment efficacy and adjustments where necessary. Patient adherence to a prescribed treatment plan is necessary for improving symptoms on the skin and overall health.
Lifestyle Modifications and Skin Care Routines
Adopting a healthy lifestyle and establishing proper skin care routines are essential for managing hypothyroidism and its skin-related symptoms. Regular exercise and a balanced diet can improve overall well-being and skin health.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Use gentle, hypoallergenic skin care products.
- Protect your skin from extreme temperatures and harsh chemicals.
- Ensure adequate sleep to promote skin repair and regeneration.
It’s important to One should remember that medical treatments are only part of what a lifestyle change can do, which could boost the quality of life for people with hypothyroidism.
Patients should also think about the clothes they wear, opting for soft, breathable materials in order to avoid any irritation. It may also help to have stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises to reduce symptoms.
Support Groups and Resources for Hypothyroid Patients
Living with hypothyroidism can be a challenge, but patients don’t have to face it alone. Support groups and resources are invaluable for coping with the condition. These groups offer a platform where one can share experiences, provide emotional support, and exchange practical tips on the management of symptoms and treatment.
- Online forums and communities
- Local support groups
- Thyroid disease advocacy organizations
- Educational websites and webinars
It’s essential for patients to stay informed and connected. Support groups can help reduce feelings of isolation and empower patients to take an active role in their health care journey.
Patients should consult with their healthcare providers for recommendations on the best resources tailored to their specific needs. Engaging with these communities can also provide insights into the latest research and treatment options, making it easier to navigate the complexities of hypothyroidism.
Long-term Monitoring and Follow-up Care
The management of hypothyroidism is a lifelong commitment that involves regular monitoring and follow-up care. Testing needs to be done periodically to ascertain if the hormonal levels are within the target range. Further adjustments to the medication will be warranted depending on these test results.
- Regular check-ups with an endocrinologist
- Consistent use of prescribed medication
- Monitoring for changes in skin condition
- Awareness of symptoms indicating hormonal imbalance
it is important that patients keep a proper communication line with their healthcare providers. It is vital that patients report new symptoms or changes in their well-being to enable timely adjustments of the treatment plans.
Conclusion
In summary, lustrous-colored stains on your hands, especially if they develop overnight, are not likely directly indicative of hypothyroidism. It can stem from the dryness and cracking associated with hypothyroidism, which might result in a more obvious stain. If you experience stains and are showing other symptoms of hypothyroidism (fatigue, weight gain, etc.), consult your physician to rule out any underlying conditions and get the proper treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1. Can hypothyroidism cause skin changes?
Yes, hypothyroidism can lead to a variety of skin changes, including dryness, coarseness, and sometimes discoloration, due to the hormonal imbalance it causes.
Q.2. Why might rust-colored stains appear on the hands overnight?
The rusty stains on the hands could be associated with various factors, be they the result of external substances, dermatological conditions, or systemic diseases like hypothyroidism.
Q.3. What tests are used to diagnose hypothyroidism?
Usually, hypothyroidism is diagnosed by using your blood and measuring thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroxine (T4) levels.
Q.4. How does thyroid hormone replacement therapy help with skin changes?
Replacement therapy of the thyroid hormones helps to normalize the levels of these hormones and ameliorate skin symptoms consequent upon hypothyroidism.
Q.5. What lifestyle modifications can help manage hypothyroidism-related skin symptoms?
Lifestyle modifications that include proper diet, hydration, and regular moisturization can help manage skin symptoms associated with hypothyroidism.
Q.5. How important is long-term monitoring for managing hypothyroidism?
Long-term monitoring is crucial in the management of hypothyroidism; it helps in adjusting the treatment plan and in detecting any changes in the condition early.